Single-nuclei multiomics analysis identifies abnormal cardiomyocytes in a murine model of cardiac development
- PMID: 40721580
- PMCID: PMC12304165
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62208-9
Single-nuclei multiomics analysis identifies abnormal cardiomyocytes in a murine model of cardiac development
Abstract
Transcription factors such as Tbx5, Gata4, Mef2c and Pitx2 are required during cardiac development, and in adult cardiac homeostasis. We demonstrate that the gene dosage and modulation of these factors are mediated in vivo by the miR-200 family. Inhibition of a single miR-200 family member within the cluster results in defects of the left ventricle and cardiomyocyte maturation during development. Inhibition of the entire miR-200 family results in a ventricular septal defect and embryonic lethality by embryonic day (E)16.5. Inhibition of each miR-200 family has distinct heart phenotypes in cell specific differentiation and maturation. snRNA-sequencing reveals an immature cardiomyocyte cell state, suggesting reduced differentiation of these cells. The miR-200 family members are critical regulators of early cardiac development through maintaining cardiomyocyte differentiation and maturation. In this report, we identify several transcription factors regulated by miR-200 during heart development, a role for miR-200 in specific heart defects, and an abnormal cardiomyocyte population.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Brad A. Amendt is the CSO and founder of NaturemiRI, LLC. All other authors have no disclosures to report.
Figures
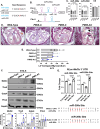
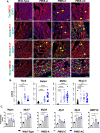


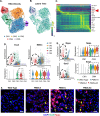
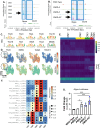
References
-
- Bruneau, B. G. et al. Chamber-specific cardiac expression of Tbx5 and heart defects in Holt–Oram syndrome. Dev. Biol.211, 100–108 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Bruneau, B. G. et al. A Murine model of Holt-Oram syndrome defines roles of the T-Box transcription factor Tbx5 in cardiogenesis and disease. Cell106, 709–721 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Liu, C. et al. Pitx2c patterns anterior myocardium and aortic arch vessels and is required for local cell movement into atrioventricular cushions. Development129, 5081–5091 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Molkentin, J. D., Lin, Q., Duncan, S. A. & Olson, E. N. Requirement of the transcription factor GATA4 for heart tube formation and ventral morphogenesis. Genes Dev.11, 1061–1072 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Garg, V. et al. GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5. Nature424, 443–447 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

