Novel loop structure of human IgG1 Fc fused CD38 targeted bispecific antibodies and their anti-tumor effect in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 40721809
- PMCID: PMC12306004
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06827-2
Novel loop structure of human IgG1 Fc fused CD38 targeted bispecific antibodies and their anti-tumor effect in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) still lacks an ideal immunotherapy target. CD38 serves as a potential therapeutic target for AML. Classical bispecific antibody (BsAb) requires continuous infusion due to small molecular size and short half-life.
Methods: The anti-human CD38 single-chain variable fragment (scFv) and anti-human CD3 scFv were cloned to expression plasmids. ExpiCHO-S cells were transfected, and the anti-CD38/anti-CD3 bispecific antibody (38-3-BsAbs) in CHO supernatants was efficiently purified. The anti-AML efficacy of 38-3-BsAbs was evaluated in vitro and in vivo.
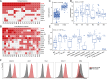
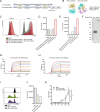
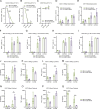
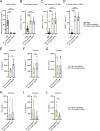
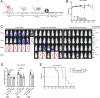
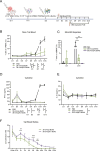
Results: The novel loop structures of non-human IgG Fc fused and human IgG1 Fc fused anti-CD38/anti-CD3 BsAbs, 38-3-loop-BsAb and 38-3-loopFc-BsAb, were designed and produced. Both 38-3-loop-BsAb and 38-3-loopFc-BsAb showed excellent anti-AML effects at low concentrations in vitro. AML xenograft NOD-scid IL2gammanull (NSG) mouse model was adopted to evaluate therapeutic effects of 38-3-BsAb. The anti-leukemic effect of 38-3-loopFc-BsAb was superior.
Conclusions: We report on new structures of 38-3 bispecific antibody and demonstrate their anti-tumor effect in the treatment of AML.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Bispecific antibody; CD38; Immunotherapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study of patients and animal experiments was approved by the Ethics Review Board of IHCAMS. All patients and health donors were informed, and written consents were signed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

