Acute and subacute toxicity of the aqueous extract of Cissus Polyantha Glig and Bradt (Vitaceae) on biochemical and hematological parameters in Wistar rats
- PMID: 40722010
- PMCID: PMC12302864
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-025-05027-1
Acute and subacute toxicity of the aqueous extract of Cissus Polyantha Glig and Bradt (Vitaceae) on biochemical and hematological parameters in Wistar rats
Abstract
Background: Cissus polyantha (C. polyantha) Glig and Bradt is a climbing plant of the Vitaceae family generally distributed in tropical regions and used in traditional African pharmacopoeia for the treatment of conjunctivitis, pain, inflammation, microbial diseases and diabetes mellitus. The aim of this study was to evaluate the acute and subacute toxicity of the aqueous extract from leafy stems of C. polyantha (AECP) in rats.
Methods: In acute toxicity, AECP was administered orally at a single dose of 2000 mg/kg. Clinical signs, general behavior and mortality were assessed for 14 days. In subacute toxicity, AECP at 111, 222 and 444 mg/kg was administered orally for 28 days. Body weight, internal organ weight, water intake, food consumption, biochemical parameters, hematological profile and histological examinations were evaluated.
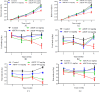
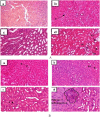
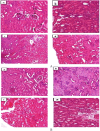
Results: Acute toxicity results showed no signs of poisoning and no mortality. The mean lethal dose (LD50) of AECP was therefore greater than 2000 mg/kg. In subacute toxicity, a significant increase in body weight, water and food consumption, liver weight and lymphocyte counts as well as a decrease in ALT activity and creatinine levels were recorded in rats of both sexes treated at 222 and/or 444 mg/kg. AECP caused a notable reduction in uric acid, total cholesterol and triglycerides at all doses tested. Histopathological analysis of rat kidneys shows slight mesengial hyperplasia at 444 mg/kg. However, all other parameters evaluated did not experience significant variation after AECP administration at all doses.
Conclusions: In acute toxicity, the LD50 is greater than 2000 mg/kg, so AECP is of low toxicity. In subacute toxicity, only the dose of 444 mg/kg of AECP resulted in decreased body weight, water and food consumption, and increased liver weight, ALT activity, and lymphocyte counts. Doses below 444 mg/kg may therefore be safe.
Keywords: Cissus Polyantha; Acute toxicity; Aqueous extract; Biochemical parameters; Haematological profile; Histology; Subacute toxicity; Wistar rats.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the Cameroon National Ethics Committee (ref. N° FWIRB 00001954) and approved by the Bioethics Advisory Commission of the Faculty of Sciences, University of Maroua (ref: No14/0261/Uma/D/FS/VD-RC). Informed consent was also sought from all study participants prior to inclusion in the study. Consent to publish: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute and Subacute Toxicity Study of α-Arbutin: An In Vivo Evidence.J Appl Toxicol. 2025 Oct;45(10):2020-2041. doi: 10.1002/jat.4822. Epub 2025 May 30. J Appl Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40443353
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Prenatal Development Studies of 2-((1-(4-Phenoxyphenoxy)propan-2-yl)oxy)pyridine (CASRN 95737-68-1) in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats and New Zealand White (Hra:NZW SPF) Rabbits: DART Report 07 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. PMID: 35593777 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The investigation on an ethnic medicinal plant of Elsholtiza bodinieri Vaniot: Chemical constituents, acute, 28-day subacute and 90-day subchronic toxicity evaluation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118635. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118635. Epub 2024 Jul 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39074518
-
Comprehensive phytochemical characterization, antioxidant potency, and toxicological evaluation of Paederia foetida in Wistar albino rats: Insights into therapeutic efficacy and safety profiles.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Aug 13;353(Pt B):120382. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120382. Online ahead of print. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40816589
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannerman RH. Traditional medicine in modern health care. WHF. 1982;3:8–13.
-
- Burkill H. The useful plants of west tropical Africa, 2nd edition. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, UK, 1985.
-
- Sani Y, Abdullahi I, Shehu M, Abdullahi U, Hanwa O, Adeiza U, Pateh U, Haruna A. Phytochemical and antimicrobial studies of methanol crude extract of the leaves of Cissus Polyantha (Vitaceae). Niger J Pharm Sci. 2013;12:35–40.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

