Overall Survival and Complication Rates in the Treatment of Liver Carcinoma: A Comparative Study of Ultrasound, Computed Tomography, and Combined Ultrasound and Computed Tomography Guidance for Radiofrequency Ablation
- PMID: 40722504
- PMCID: PMC12293419
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15141754
Overall Survival and Complication Rates in the Treatment of Liver Carcinoma: A Comparative Study of Ultrasound, Computed Tomography, and Combined Ultrasound and Computed Tomography Guidance for Radiofrequency Ablation
Abstract
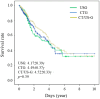
Background: Liver cancer is a major health concern worldwide. Radiofrequency ablation is a safe treatment option that can be guided by either ultrasound, computer tomography (CT), or fluoroscopy. Although ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation is commonly used in clinical practice, radiofrequency ablation guided by CT is more precise but requires more time and does not offer real-time monitoring, which may result in complications such as pneumothorax or organ damage. Objectives: In this study, we investigated the effect of ultrasound, CT, and combined ultrasound/CT guidance on patient survival and complication development. Methods: A total of 982 radiofrequency ablation sessions conducted on 553 patients were analyzed. Clinical outcomes were assessed during follow-up to determine the survival and recurrence rates of malignant tumors. Results: Overall, the three guidance approaches exhibited significant differences in terms of tumor size, number, complication development, and treatment duration. However, no significant differences were observed in survival rate. A comparison of the effect of CT guidance and ultrasound guidance on complication development revealed a higher odds ratio for CT guidance in some cases. A comparison of combined ultrasound/CT guidance and ultrasound guidance revealed nonsignificant differences in complication development. A comparison of CT guidance and combined ultrasound/CT guidance revealed a higher odds ratio for CT guidance in some cases. Radiofrequency ablation is a safe and effective treatment for liver tumors. However, CT has an increased incidence of complications. Conclusions: Combined ultrasound/computer tomography guidance is recommended for patients with multiple or large tumors or tumors near the hepatic dome or diaphragm.
Keywords: CT-guided; HCC; US-guided; US/CT-guided; radiofrequency ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ablative and non-surgical therapies for early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2023 Dec;27(29):1-172. doi: 10.3310/GK5221. Health Technol Assess. 2023. PMID: 38149643 Free PMC article.
-
Endovenous ablation therapy (laser or radiofrequency) or foam sclerotherapy versus conventional surgical repair for short saphenous varicose veins.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 29;11(11):CD010878. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010878.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27898181 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided versus anatomic landmark-guided percutaneous femoral artery access.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 28;3(3):CD014594. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014594.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40152297
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
PET-CT for assessing mediastinal lymph node involvement in patients with suspected resectable non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 13;2014(11):CD009519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009519.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25393718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cha D.I., Lee M.W., Hyun D., Ahn S.H., Jeong W.K., Rhim H. Combined transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma infeasible for ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: A comparative study with general ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation outcomes. Cancers. 2023;15:5193. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215193. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee L.H., Hwang J.I., Cheng Y.C., Wu C.Y., Lee S.W., Yang S.S., Yeh H.Z., Chang C.S., Lee T.Y. Comparable outcomes of ultrasound versus computed tomography in the guidance of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0169655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169655. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huo J., Aloia T.A., Xu Y., Chung T.H., Sheu T., Shih Y.C.T. Comparative effectiveness of CT- vs. ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation among medicare patients 65 years of age or older with hepatocellular carcinoma. Value Health. 2018;22:284–292. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2018.10.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources