Steatosis and Interferon Associated with HBsAg Immune Control in Chronic Hepatitis B: A Real-World Propensity Score-Matched Study
- PMID: 40722612
- PMCID: PMC12292579
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13071538
Steatosis and Interferon Associated with HBsAg Immune Control in Chronic Hepatitis B: A Real-World Propensity Score-Matched Study
Abstract
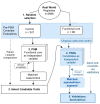
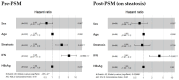
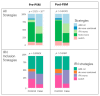
Background/Objectives: The baseline determinants of functional cure in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) are largely unknown. By applying propensity score matching (PSM) to real-world data, we aimed to identify traits associated with functional cure. Methods: We included CHB cases which achieved a functional cure and randomly selected non-achievers from patients followed from 2000 to 2020. Initial screening of baseline candidate traits was conducted using PSM-balanced cases and controls. Subsequently, through multiple rounds of leave-one-covariate-out on the balanced cohorts, we validated the impact of these traits using survival analysis. Results: In total, 85 cases (mean age: 35.78; female/male: 23/62) were compared with 247 controls (mean age: 37.08; female/male: 80/167, out of 3666), with a median follow-up of 69.56 months. Steatosis and interferon (IFN) treatment were significantly more frequent in the cases, as confirmed by forest plots showing significant hazard ratios. During validation, whether through balancing all covariates or leave-one-covariate-out matching, both steatosis and exposure to IFN resulted in a higher number of functional cures and HBsAg seroconversions. Further comparisons revealed that add-on or monotherapy outperformed switching (from IFN to NUC), while the de novo (IFN + NUC, followed by NUC) approach was not observed. Conclusions: We confirmed that individuals with steatosis at baseline or those who received IFN were more likely to achieve HBsAg immune control, with monotherapy/add-on therapy being emphasized.
Keywords: HBsAg seroconversion; functional cure; interferon; propensity score matching; steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Cornberg M., Lok A.S.-F., Terrault N.A., Zoulim F. 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference Faculty. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B—Report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference (double dagger) J. Hepatol. 2020;72:539–557. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.11.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hosaka T., Suzuki F., Akuta N., Sezaki H., Suzuki Y., Kawamura Y., Kobayashi M., Saitoh S., Arase Y., Ikeda K., et al. Seroclearance rate of hepatitis B surface antigen in 2112 patients with chronic hepatitis in Japan during long-term follow-up. J. Gastroenterol. 2014;49:538–546. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

