Cerebral Edema in Traumatic Brain Injury
- PMID: 40722798
- PMCID: PMC12292430
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13071728
Cerebral Edema in Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
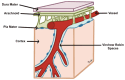
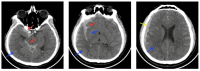
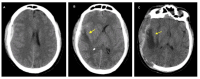
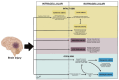
Cerebral edema is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in any of the tissue compartments of the cerebral parenchyma. It remains a significant challenge in neurotrauma care because it contributes to secondary brain injury, affecting prognosis. This review analyzes the recent literature, including foundational studies, to describe the mechanisms of distinct types of cerebral edema following traumatic brain injury (TBI). Emerging concepts, such as the role of the glymphatic system and heme-derived inflammasomes, offer new insights into new types of edemas, differentiated by pathogenesis and potential treatments. Recent advancements in understanding these molecular mechanisms can improve therapeutic strategies, facilitating a better approach in the era of precision and personalized medicine. Although there has been notable progress, a proposal to customize treatments for diverse types of edemas is necessary to improve outcomes following traumatic brain injury. In this review, we describe the current subtypes of post-traumatic brain edemas and link them to a specific management approach.
Keywords: aquaporins; blood–brain barrier; cerebral edema; glymphatic system; intracranial pressure; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

