The Link Between Left Atrial Longitudinal Reservoir Strain and Mitral Annulus Geometry in Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 40722823
- PMCID: PMC12292555
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines13071753
The Link Between Left Atrial Longitudinal Reservoir Strain and Mitral Annulus Geometry in Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
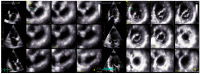
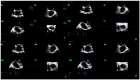
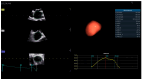
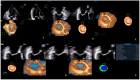
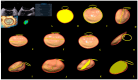
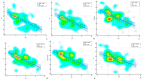
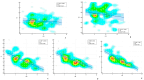
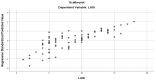
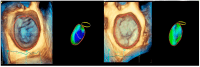
Background/Objectives: Anatomical and functional damage of the mitral valve (MV) apparatus in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is secondary to left ventricular (LV) injury, leading to functional mitral regurgitation (FMR). Real-time four-dimensional echocardiography (RT 4DE) is a useful imaging technique in different pathologies, including DCM. Left atrial (LA) strain, as measured by left atrium quantification software, is an accurate technique for evaluating increased filling pressure. The MV has a complex three-dimensional morphology and motion. Four-dimensional echocardiography (4DE) has revolutionized clinical imaging of the mitral valve apparatus. This study aims (1) to characterize the mitral annulus (MA) parameters in patients with DCM and advanced-stage heart failure (HF) according to etiology and (2) to find correlations between left atrial function and MA remodeling in this group of patients, using 4DE quantification software. Methods: A total of 82 patients with DCM and an LV ejection fraction ≤ 40% were recruited. Conventional 2DE and RT 4DE were conducted in DCM patients with a compensated phase of HF before discharge. The measured parameters were left atrial reservoir strain (LASr), annular area (AA), annular perimeter (AP), anteroposterior diameter (A-Pd), posteromedial to anterolateral diameter (PM-ALd), commissural distance (CD), interregional distance (ITD), annular height (AH), nonplanar angle (NPA), tenting height (TH), tenting area (TA), and tenting volume (TV). Results: Measured parameters revealed more advanced damage of LA and MA parameters in ischemic compared to nonischemic etiology. Univariate analysis identified AA, AP, A-Pd, PM-ALd, CD, ITD, TH, TA, and TV (p < 0.0001) as determinants of LASr. Including these parameters in a stepwise multivariate logistic regression, PM-ALd (p = 0.03), TH (p = 0.043), and TV (p = 0.0001) were the best predictors of LAsr in these patients. Conclusions: The results of this study revealed the correlation between LA function depression and MA remodeling in patients with DCM.
Keywords: dilated cardiomyopathy; four-dimensional echocardiography; functional mitral regurgitation; left atrial reservoir strain; mitral annulus remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Donal E., Delgado V., Bucciarelli-Ducci C., Galli E., Haugaa K., Charron P., Voigt J.-U., Cardim N., Masci P.G., Galderisi M., et al. Multimodality imaging in the diagnosis, risk stratification, and management of patients with dilated cardiomyopathies: An expert consensus document from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2019;20:1075–1093. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jez178. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

