Non-Bovine Milk as Functional Foods with Focus on Their Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivities
- PMID: 40722905
- PMCID: PMC12291644
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14070801
Non-Bovine Milk as Functional Foods with Focus on Their Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivities
Abstract
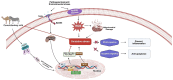
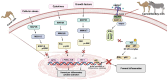
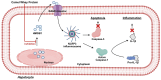
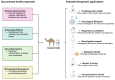
The growing interest in functional foods has directed scientific attention toward alternative milk sources, particularly camel and donkey milk, which have been traditionally consumed for their purported health benefits across diverse cultures. These milk sources possess unique nutritional profiles and bioactive compositions that differ substantially from conventional bovine milk. This review examines the current scientific understanding of the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant bioactivities of camel and donkey milk, exploring their bioactive constituents and therapeutic potential. Camel and donkey milk demonstrate notable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may exceed those of conventional milk sources. Key bioactive compounds include lactoferrin, lysozyme, immunoglobulins, bioactive peptides, vitamins C and E, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. Mechanistic studies reveal that milk from donkeys and camels suppresses inflammatory pathways through NF-κB inhibition, cytokine modulation (reducing IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α while enhancing IL-10), and antioxidant pathway activation via Nrf2-ARE signaling. Donkey milk exhibits particularly high lysozyme content and demonstrates significant immunomodulatory effects, while camel milk shows remarkable therapeutic potential in diabetes management, nephroprotection, and hepatoprotection. Preclinical studies demonstrate efficacy in treating oxidative stress-related disorders, inflammatory conditions, metabolic dysfunction, and tissue injury models. Altogether, the published data show that camel and donkey milk represent promising functional foods with significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory bioactivities mediated through multiple molecular pathways. Their unique bioactive profiles offer therapeutic potential for various health conditions, warranting further clinical investigation and development as nutraceutical interventions.
Keywords: antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities; bioactive compounds; camel milk; donkey milk; functional foods; therapeutic potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory potential of dietary soybean-derived saponins.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae349. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae349. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39529449 Review.
-
A state-of-art review on camel milk proteins as an emerging source of bioactive peptides with diverse nutraceutical properties.Food Chem. 2022 Mar 30;373(Pt A):131444. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131444. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 34717085
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico analysis of polyphenols modulate bovine PPARγ to increase milk fat synthesis in dairy cattle via the MAPK signaling pathways.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae248. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae248. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39210246
-
The multifaceted therapeutic properties of camel milk: from neuroprotection to anti-cancer effects.J Food Sci Technol. 2025 May;62(5):824-840. doi: 10.1007/s13197-025-06264-5. Epub 2025 Mar 18. J Food Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40182673 Review.
References
-
- Xie A., Shen X., Hong R., Xie Y., Zhang Y., Chen J., Li Z., Li M., Yue X., Quek S.Y. Unlocking the potential of donkey milk: Nutritional composition, bioactive properties and future prospects. Food Res. Int. 2025;209:116307. - PubMed
-
- Derdak R., Sakoui S., Pop O.L., Muresan C.I., Vodnar D.C., Addoum B., Vulturar R., Chis A., Suharoschi R., Soukri A., et al. Insights on health and food applications of Equus asinus (donkey) milk bioactive proteins and peptides—An overview. Foods. 2020;9:1302. doi: 10.3390/foods9091302. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 2022YFD1600103; 2023YFD1302004/National Key R&D Program of China
- SDAIT-27/Shandong Province Modern Agricultural Technology System Donkey Industrial Innovation Team
- 19211162/Livestock and Poultry Breeding Industry Project of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs
- ZR2024MC130/Shandong Province Agricultural Major Technology Collaborative Promotion Plan
- GDWZ202401/Liaocheng Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology, High-talented Foreign Expert Introduction Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

