Unveiling the Cardioprotective Potential of Hydroxytyrosol: Insights from an Acute Myocardial Infarction Model
- PMID: 40722907
- PMCID: PMC12291871
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14070803
Unveiling the Cardioprotective Potential of Hydroxytyrosol: Insights from an Acute Myocardial Infarction Model
Abstract
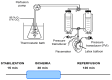
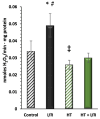
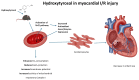
Cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies. The Mediterranean diet is renowned for its cardiovascular benefits, largely attributed to extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) and its phenolic compounds, particularly hydroxytyrosol (HT). HT, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, has demonstrated significant therapeutic potential in mitigating myocardial damage following acute myocardial infarction (AMI). However, there is a notable lack of published evidence regarding the effects of HT administration in the context of acute ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, making this study a novel contribution to the field. This study aimed to evaluate the cardioprotective effects of HT using the Langendorff technique in an isolated mouse heart ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) model. Mice were administered a single intraperitoneal dose of HT (10 mg/kg) 24 h prior to the I/R protocols, and parameters such as the infarct size, mitochondrial function, and redox balance were assessed. The results revealed a remarkable 57% reduction in infarct size in HT-treated mice compared to untreated controls. HT treatment also improved mitochondrial bioenergetics, as evidenced by the increased membrane potential (ΔΨm), enhanced oxygen consumption, and reduced hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production. Furthermore, HT restored the activity of the mitochondrial respiratory complexes, notably Complex I, even under I/R conditions. These findings highlight the efficacy of HT in reducing oxidative stress and preserving mitochondrial function, critical factors in cardiac disease. In conclusion, HT emerges as a promising therapeutic agent for ischemic heart disease, demonstrating both preventive and restorative potential. Future research should explore its clinical applicability to advance cardiovascular disease management.
Keywords: antioxidant; by-products; cardioprotection; hydroxytyrosol (HT); ischemic heart disease (IHD); mitochondrial function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
N-Acetylcysteine Treatment Restores the Protective Effect of Heart Ischemic Postconditioning in a Murine Model in the Early Stages of Atherosclerosis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;18(7):1014. doi: 10.3390/ph18071014. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732302 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and in silico insights into the antidiabetic efficacy of EVOO and hydroxytyrosol in a rat model.J Nutr Biochem. 2025 Jan;135:109775. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109775. Epub 2024 Oct 5. J Nutr Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39370013
-
High-Tyrosol/Hydroxytyrosol Extra Virgin Olive Oil Enhances Antioxidant Activity in Elderly Post-Myocardial Infarction Patients.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jul 16;14(7):867. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070867. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722971 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AL-Asmari1 K.M., Al-Attar A.M., Abu Zeid I.M. Potential health benefits and components of oliveoil: An overview. Biosci. Res. 2020;17:2673–2687.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

