Carnosol, a Rosemary Ingredient Discovered in a Screen for Inhibitors of SARM1-NAD+ Cleavage Activity, Ameliorates Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
- PMID: 40722912
- PMCID: PMC12291994
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14070808
Carnosol, a Rosemary Ingredient Discovered in a Screen for Inhibitors of SARM1-NAD+ Cleavage Activity, Ameliorates Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
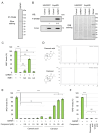
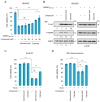
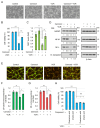
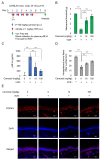
Sterile alpha and Toll/interleukin receptor motif-containing protein 1 (SARM1) is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) hydrolase involved in axonal degeneration and neuronal cell death. SARM1 plays a pivotal role in triggering the neurodegenerative processes that underlie peripheral neuropathies, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative diseases. Importantly, SARM1 knockdown or knockout prevents the degeneration; as a result, SARM1 has been attracting attention as a potent therapeutic target. In recent years, the development of several SARM1 inhibitors derived from synthetic chemical compounds has been reported; however, no dietary ingredients with SARM1 inhibitory activity have been identified. Therefore, we here focused on dietary ingredients and found that carnosol, an antioxidant contained in rosemary, inhibits the NAD+-cleavage activity of SARM1. Purified carnosol inhibited the enzymatic activity of SARM1 and suppressed neurite degeneration and cell death induced by the anti-cancer medicine vincristine (VCR). Carnosol also inhibited VCR-induced hyperalgesia symptoms, suppressed the loss of intra-epidermal nerve fibers in vivo, and reduced the blood fluid level of phosphorylated neurofilament-H caused by an axonal degeneration event. These results indicate that carnosol has a neuroprotective effect via SARM1 inhibition in addition to its previously known antioxidant effect via NF-E2-related factor 2 and thus suppresses neurotoxin-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Keywords: NAD+; SARM1; axon degeneration; carnosol; peripheral neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors, Hitoshi Murata, Kazuki Ogawa, Yoji Wada, Hiromichi Nakamura, and Masakiyo Sakaguchi have filed a patent application for the research in this article. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with respect to the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SARM1: The Checkpoint of Axonal Degeneration in the Nervous System Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul;62(7):9240-9257. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04835-3. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40097763 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A SARM1-mitochondrial feedback loop drives neuropathogenesis in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A rat model.J Clin Invest. 2022 Dec 1;132(23):e161566. doi: 10.1172/JCI161566. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 36287202 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of Sarm1 attenuates expression and mislocalization of phosphorylated TDP-43 after mouse repetitive traumatic brain injury.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Dec 20;11(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01709-4. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 38124145 Free PMC article.
-
SARM1 Exacerbates Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Heart Failure by Enhancing NAD+ Metabolism.FASEB J. 2025 Jul 31;39(14):e70808. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500486RR. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40662942 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

