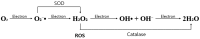Expression of Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species in Endometriosis: Current Knowledge and Its Implications
- PMID: 40722981
- PMCID: PMC12292080
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14070877
Expression of Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species in Endometriosis: Current Knowledge and Its Implications
Abstract
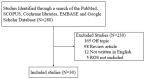
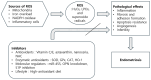
This review explores the dual role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, aiming to deepen our understanding of these processes through a systematic literature review. To assess the induction and involvement of ROS in endometriosis, we conducted a comprehensive literature review using Cochrane Libraries, EMBASE, Google Scholar, PubMed, and SCOPUS databases. Of 30 qualifying papers ultimately reviewed, 28 reported a significant contribution of ROS to the pathogenesis of endometriosis, while two found no association. The presence of ROS in endometriosis is associated with infertility, irregular menstrual cycles, painful menstruation, and chronic pelvic discomfort. Among individual ROS types studied, hydrogen peroxide was most frequently investigated, followed by lipid peroxides and superoxide radicals. Notable polymorphisms associated with ROS in endometriosis include those for AT-rich interactive domain 1A (ARID1A) and quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) isoforms. Key enzymes for ROS scavenging and detoxification include superoxide dismutase, glutathione, and glutathione peroxidase. Effective inhibitors of ROS related to endometriosis are vitamins C and E, astaxanthin, fatty acid-binding protein 4, cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria), osteopontin, sphingosine 1-phosphate, N-acetyl-L-cysteine, catalase, and a high-antioxidant diet. Elevated levels of ROS and free radicals are involved in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, suggesting that targeting these molecules could offer potential therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: endometriosis; free radicals; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 5;(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. PMID: 23913583 Updated.
-
Endometrial biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 20;4(4):CD012165. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012165. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27094925 Free PMC article.
-
Blood biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 1;2016(5):CD012179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012179. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27132058 Free PMC article.
-
Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) for symptomatic endometriosis following surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 20;12(12):CD005072. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005072.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34928503 Free PMC article.
-
Oral contraceptives for pain associated with endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 22;5(5):CD001019. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001019.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29786828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sampson J.A. Peritoneal endometriosis due to menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the pelvic cavity. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1927;14:422–469. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(15)30003-X. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous