Pemafibrate Ameliorates Steatotic Liver Disease Regardless of Endothelial Dysfunction in Mice
- PMID: 40722995
- PMCID: PMC12292507
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14070891
Pemafibrate Ameliorates Steatotic Liver Disease Regardless of Endothelial Dysfunction in Mice
Abstract
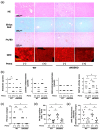
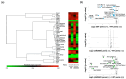
Endothelial dysfunction contributes to the progression of metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Pemafibrate has been shown to ameliorate MASLD in basic and clinical studies, but it is unclear whether it is also effective in the status of endothelial dysfunction. An MASLD animal model was induced in male wild-type (WT) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-deficient (eNOSKO) mice by feeding them a high-fat/cholesterol/cholate diet, and they were administered either a vehicle or pemafibrate at 0.17 mg/kg/day for 10 weeks. Although pemafibrate treatment did not change plasma lipid profiles in either WT or eNOSKO mice, pemafibrate reduced plasma AST levels in both WT and eNOSKO mice compared to the levels in the vehicle-treated mice. Histopathological analysis of the liver showed that MASLD was improved in the pemafibrate-treated groups in both WT and eNOSKO mice. Compared to vehicle treatment, pemafibrate treatment significantly reduced the expression levels of hepatic NADPH oxidase subunit genes, M1 macrophages, inflammatory-cytokine-related genes and profibrotic genes in both WT and eNOSKO mice, along with reduction in hepatic oxidative stress assessed by dihydroethidium staining and 4-hydroxynonenal protein levels. Thus, pemafibrate ameliorated MASLD with reduction in oxidative stress and inflammation even in vascular endothelial dysfunction.
Keywords: MASLD; NADPH oxidase; eNOS; endothelial dysfunction; oxidative stress; pemafibrate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Pemafibrate on LDL-C and Related Lipid Markers in Patients with MASLD: A Sub-Analysis of the PEMA-FL Study.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2025 Jul 1;32(7):823-839. doi: 10.5551/jat.65395. Epub 2024 Dec 18. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2025. PMID: 39694503 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment with pemafibrate ameliorates fatty liver index and atherogenic lipid profiles in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 17;16:1496671. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1496671. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40747315 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aerobic-Resistance Training with Royal Jelly Supplementation Has a Synergistic Effect on Paraoxonase 1 Changes and Liver Function in Women with MASLD.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Feb 17;61(2):349. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020349. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40005465 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Silymarin for adults with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 24;6(6):CD015524. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015524.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40552569
References
-
- Angulo P., Kleiner D.E., Dam-Larsen S., Adams L.A., Bjornsson E.S., Charatcharoenwitthaya P., Mills P.R., Keach J.C., Lafferty H.D., Stahler A., et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated with Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:389–397.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

