Integrating 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT with Clinical Risk Factors for Enhanced Prostate Cancer Progression Prediction
- PMID: 40723170
- PMCID: PMC12293663
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17142285
Integrating 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT with Clinical Risk Factors for Enhanced Prostate Cancer Progression Prediction
Abstract
Background/objectives: This study evaluates whether combining 68Ga-PSMA-11-PET/CT derived imaging biomarkers with clinical risk factors improves the prediction of early biochemical recurrence (eBCR) or clinical progress in patients with high-risk prostate cancer (PCa) after primary treatment, using machine learning (ML) models.
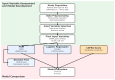
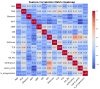
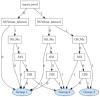
Methods: We analyzed data from 93 high-risk PCa patients who underwent 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT and received primary treatment at a single center. Two predictive models were developed: a logistic regression (LR) model and an ML derived probabilistic graphical model (PGM) based on a naïve Bayes framework. Both models were compared against each other and against the CAPRA risk score. The models' input variables were selected based on statistical analysis and domain expertise including a literature review and expert input. A decision tree was derived from the PGM to translate its probabilistic reasoning into a transparent classifier.
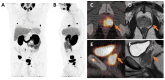
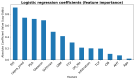
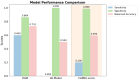
Results: The five key input variables were as follows: binarized CAPRA score, maximal intraprostatic PSMA uptake intensity (SUVmax), presence of bone metastases, nodal involvement at common iliac bifurcation, and seminal vesicle infiltration. The PGM achieved superior predictive performance with a balanced accuracy of 0.73, sensitivity of 0.60, and specificity of 0.86, substantially outperforming both the LR (balanced accuracy: 0.50, sensitivity: 0.00, specificity: 1.00) and CAPRA (balanced accuracy: 0.59, sensitivity: 0.20, specificity: 0.99). The decision tree provided an explainable classifier with CAPRA as a primary branch node, followed by SUVmax and specific PET-detected tumor sites.
Conclusions: Integrating 68Ga-PSMA-11 imaging biomarkers with clinical parameters, such as CAPRA, significantly improves models to predict progression in patients with high-risk PCa undergoing primary treatment. The PGM offers superior balanced accuracy and enables risk stratification that may guide personalized treatment decisions.
Keywords: 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT; CAPRA score; SUVmax; early biochemical recurrence; outcome prediction; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Machine learning-based construction and validation of an radiomics model for predicting ISUP grading in prostate cancer: a multicenter radiomics study based on [68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET/CT.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Jun 24. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07412-x. Online ahead of print. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40553115
-
Tumor Segmentation on PSMA PET/CT Predicts Survival in Biochemical Recurrence of Prostate Cancer: A Retrospective Study Using [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 and [18F]-PSMA-1007.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 4;17(13):2249. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132249. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647545 Free PMC article.
-
PSMA-PET-derived distance features as biomarkers for predicting outcomes in primary prostate cancer post-radical prostatectomy.Cancer Imaging. 2025 Jul 22;25(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40644-025-00907-8. Cancer Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40696478 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Role of Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Primary Staging before Definitive Treatment.Eur Urol. 2025 Jun;87(6):654-671. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2025.03.003. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Eur Urol. 2025. PMID: 40155242
-
PET-CT for assessing mediastinal lymph node involvement in patients with suspected resectable non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 13;2014(11):CD009519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009519.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25393718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cornford P., Bergh R., Briers E., Van den Broeck T., Brunckhorst O., Darraugh J., Eberli D., Meerleer G., Santis M., Farolfi A., et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer—2024 Update. Part I: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2024;86:148–163. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2024.03.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cornford P., Bergh R., Briers E., Van den Broeck T., Cumberbatch M., Santis M., Fanti S., Fossati N., Gandaglia G., Gillessen S., et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II-2020 Update: Treatment of Relapsing and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2020;79:263–282. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.046. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

