Chimeric Element-Regulated MRI Reporter System for Mediation of Glioma Theranostics
- PMID: 40723232
- PMCID: PMC12293648
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17142349
Chimeric Element-Regulated MRI Reporter System for Mediation of Glioma Theranostics
Abstract
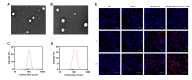
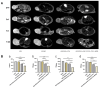
Background and Purpose: Glioblastoma remains a therapeutic challenge with a poor prognosis despite multimodal treatments. Reporter-based magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers a promising approach for tumor visualization, but its efficacy depends on sufficient reporter gene expression. This study aimed to develop a chimeric element-regulated ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1) reporter system to enhance MRI-based glioma detection while enabling targeted therapy via transferrin receptor (TfR)-mediated drug delivery. Methods: Using gene cloning techniques, we constructed a chimeric FTH1 expression system comprising tumor-specific PEG3 promoter (transcriptional control), bFGF-2 5'UTR (translational enhancement), and WPRE (mRNA stabilization). Lentiviral vectors delivered constructs to U251 glioblastoma cells and xenografts. FTH1/TfR expression was validated by Western blot and immunofluorescence. Iron accumulation was assessed via Prussian blue staining and TEM. MRI evaluated T2 signal changes. Transferrin-modified doxorubicin liposomes (Tf-LPD) were characterized for size and drug loading and tested for cellular uptake and cytotoxicity in vitro. In vivo therapeutic efficacy was assessed in nude mouse models through tumor volume measurement, MR imaging, and histopathology. Results: The chimeric system increased FTH1 expression significantly over PEG3-only controls (p < 0.01), with an increase of nearly 1.5-fold compared to the negative and blank groups and approximately a two-fold increase relative to the single promoter group, with corresponding TfR upregulation. Enhanced iron accumulation reduced T2 relaxation times significantly (p < 0.01), improving MR contrast. Tf-LPD (115 nm, 70% encapsulation) showed TfR-dependent uptake, inducing obvious apoptosis in high-TfR cells compared with that in controls. In vivo, Tf-LPD reduced tumor growth markedly in chimeric-system xenografts versus controls, with concurrent MR signal attenuation. Conclusions: The chimeric regulatory strategy overcomes limitations of single-element systems, demonstrating significant potential for integrated glioma theranostics. Its modular design may be adaptable to other reporter genes and malignancies.
Keywords: PEG3 promoter; chimeric element-regulated; reporter gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Price M., Neff C., Cioffi G., Waite K.A., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2016–2020. Neuro Oncol. 2023;25((12 Suppl. 2)):iv1–iv99. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad149. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

