Transcriptomic and Functional Validation Reveals PAQR3/P6-55 as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 40723340
- PMCID: PMC12292340
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14070780
Transcriptomic and Functional Validation Reveals PAQR3/P6-55 as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Colon Cancer
Abstract
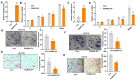
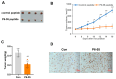
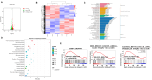
Colon cancer is one of the leading malignant tumors worldwide, and the membrane protein PAQR3 has been identified as a tumor suppressor in multiple cancers. Notably, the peptide synthesized from 6 to 55 amino acids at the N-terminal of PAQR3 (P6-55) has been shown to effectively inhibit the growth of gastric cancer cells. This study aims to elucidate the mechanism of PAQR3 and explore its therapeutic potential in colon cancer. CCK8 cell viability assays, colony formation assays, and transwell migration assays were employed to systematically assess the inhibitory effects of PAQR3 on the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells. Furthermore, we confirmed that P6-55 exhibits functional similarities to PAQR3, effectively inhibiting the growth of colon cancer in vitro and in vivo. RNA sequencing revealed that PAQR3 suppresses tumor growth via the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, providing a strong theoretical foundation for therapeutic strategies targeting PAQR3/P6-55. In conclusion, our findings highlight the therapeutic potential of PAQR3/P6-55 as novel colon cancer inhibitors.
Keywords: P6-55; PAQR3; PI3K-AKT; colon cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploring the Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Potential of Coptisine in Colon Cancer: A Network Pharmacology Approach.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(16):3295-3308. doi: 10.2174/0109298673262553231227075800. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38231070
-
Exploring potential therapeutic targets for colorectal tumors based on whole genome sequencing of colorectal tumors and paracancerous tissues.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 4;12:1605117. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1605117. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40688112 Free PMC article.
-
RSU1 Mediates Caco-2 Colorectal Cancer Cells Proliferation and Migration via PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun 21. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01809-z. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40544194
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

