Synthetic Feed Attractants in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Culture: Effects on Growth, Health, and Appetite Stimulation
- PMID: 40723523
- PMCID: PMC12291888
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15142060
Synthetic Feed Attractants in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Culture: Effects on Growth, Health, and Appetite Stimulation
Abstract
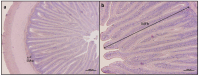
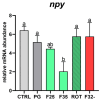
Synthetic flavors from standardized processes have recently emerged as a promising and sustainable alternative to traditional feed attractants. In this study, two attractive (F25, cheese; F35, caramel) and one repulsive (F32-, coconut) synthetic flavors were individually added (1% w/w) to a commercial diet for European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and tested over a 90-day feeding trial (30 fish per tank, in triplicate; initial weight 72.48 ± 8.04 g) to assess their impact on fish growth performance, welfare, and the modulation of brain appetite and monoaminergic pathways. None of the tested flavors negatively affected overall fish health. The F35 flavor enhanced feed intake (90.1 ± 5.6%) and growth (SGR 2.2 ± 0.2%) and positively influenced appetite-related and monoaminergic signals, thus being more effective than the F25 one (80.4 ± 3.2 and 1.6 ± 0.1%, respectively). A weekly feeding rotation between F35 and F25 (ROT group) resulted in suboptimal outcomes compared to F35 administration alone. The F32- flavor was not clearly perceived as strongly aversive by seabass and did not impair zootechnical performance. These findings highlight the potential of attractive synthetic flavors to improve diet palatability in a carnivorous species of commercial value, offering novel insights for more sustainable and cost-effective aquaculture feeding strategies.
Keywords: animal welfare; aquaculture; aquafeed; histology; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- FAO . The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024—Blue Transformation in Action. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2024.
-
- Goda A.M., El-Haroun E.R., Kabir Chowdhury M.A. Effect of Totally or Partially Replacing Fish Meal by Alternative Protein Sources on Growth of African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) Reared in Concrete Tanks. Aquac. Res. 2007;38:279–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2007.01663.x. - DOI
-
- Cashion T., Le Manach F., Zeller D., Pauly D. Most Fish Destined for Fishmeal Production Are Food-Grade Fish. Fish Fish. 2017;18:837–844. doi: 10.1111/faf.12209. - DOI
-
- Macusi E.D., Cayacay M.A., Borazon E.Q., Sales A.C., Habib A., Fadli N., Santos M.D. Protein Fishmeal Replacement in Aquaculture: A Systematic Review and Implications on Growth and Adoption Viability. Sustainability. 2023;15:12500. doi: 10.3390/su151612500. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

