Selection for Growth Performance in Oreochromis niloticus Across Different Aquatic Environments Using Growth Hormone Gene Polymorphisms
- PMID: 40723560
- PMCID: PMC12291795
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15142097
Selection for Growth Performance in Oreochromis niloticus Across Different Aquatic Environments Using Growth Hormone Gene Polymorphisms
Abstract
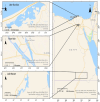
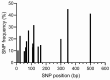
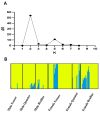
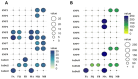
The current work focused on the molecular selection of Oreochromis niloticus with improved growth performance through marker-trait associations between SNPs within the growth hormone gene (GH) and growth performance. A total of 155 fish of the same age were collected from three locations (Lake Brullus (B), the River Nile at El-Qanater El-Khairia (Q), and Lake Nasser (A)). The selected individual progenies were evaluated through gene expression analysis for growth, inflammatory, nervous, and immune-related genes. A total of nine SNPs and three InDels were significantly associated with morphometric characteristics. The phenotypic variance (R2) of the detected SNPs ranged between 2.6% and 36%. The best populations were A and Q, as they recorded the best growth performance and harboured the highest number of SNPs and InDels, in addition to a significant increase in body weight and length. Furthermore, their progenies documented the most promising gene expression patterns of all tested genes. The current research highlights the importance of molecular selection and the potential use of population-specific SNPs in tilapia breeding programs.
Keywords: Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus); SNPs; growth hormone gene; larval gene expression; population structure; selective breeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures






References
-
- Boyd C.E., D’Abramo L.R., Glencross B.D., Huyben D.C., Juarez L.M., Lockwood G.S., McNevin A.A., Tacon A.G.J., Teletchea F., Tomasso J.R., et al. Achieving Sustainable Aquaculture: Historical and Current Perspectives and Future Needs and Challenges. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020;51:578–633. doi: 10.1111/jwas.12714. - DOI
-
- Gjedrem T., Robinson N., Rye M. The Importance of Selective Breeding in Aquaculture to Meet Future Demands for Animal Protein: A Review. Aquaculture. 2012;350–353:117–129. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.04.008. - DOI
-
- Siddique M.A.B., Mahalder B., Haque M.M., Bashar A., Hasan M.M., Shohan M.H., Talukdar M.M.N., Biswas J.C., Ahammad A.K.S. Assessment of Embryonic and Larval Development of Nile Tilapia under the Traditional and Re-Circulatory Thermostatic System in Relation to Climatic and Water Quality Variations. Aquac. J. 2023;3:70–89. doi: 10.3390/aquacj3020008. - DOI
-
- Soliman N.F., Yacout D.M.M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Status, constraints and potentials. Aquac. Int. 2016;24:1201–1227. doi: 10.1007/s10499-016-9989-9. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

