Genome-Wide Association Study of Immune Indices in Yaks
- PMID: 40723577
- PMCID: PMC12291813
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15142114
Genome-Wide Association Study of Immune Indices in Yaks
Abstract
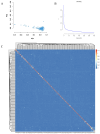
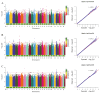
The yak is a vital livestock resource on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, renowned for its strong disease resistance and high-quality meat. However, various diseases pose significant threats to its health and lead to substantial economic losses. Current feeding management practices, along with available drugs and vaccines, have demonstrated limited effectiveness in preventing and controlling infectious diseases. Additionally, challenges such as drug resistance and the safety of animal products persist. Therefore, enhancing the disease-resistant breeding capacity of yaks is crucial. In this study, we examined 192 yaks by measuring the concentrations of 10 immune indicators in serum by using the ELISA method and conducting whole-genome resequencing, which identified 19,182,942 SNP loci. Through genome-wide association analysis, we detected 323 significant SNPs located near or within 125 candidate genes, most of which are associated with disease and significantly enriched in the TGF-β signaling pathway. Overall, our study identified a series of novel variants and candidate genes associated with disease resistance traits in yaks, providing important information for the molecular breeding of disease resistance in yaks. These results not only contribute to a deeper understanding of the function of disease resistance genes in yaks but also hold great potential for accelerating precision disease resistance breeding in yaks.
Keywords: GWAS; SNP; immune indices; resequencing; yak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bray C., Bell L.N., Liang H., Haykal R., Kaiksow F., Mazza J.J., Yale S.H. Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-reactive Protein Measurements and Their Relevance in Clinical Medicine. WMJ. 2016;115:317–321. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- XZ202402ZY0012/Tibet Autonomous Region Key Research and Development Project on the Innovative Utilization of Tibetan Wild-Blooded Yak and Jila Yak Germplasm
- CARS-37/Modern Beef Yak Industry Technology System
- 25-LIHPS-01/Yak Resources and Breeding Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
- QYXTZX-RKZ2022-03/Tibet Autonomous Region Regional Science and Technology Collaborative Innovation Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

