Female Reproductive Tract Organoids: Applications from Physiology to Pathology
- PMID: 40723797
- PMCID: PMC12292772
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15070925
Female Reproductive Tract Organoids: Applications from Physiology to Pathology
Abstract
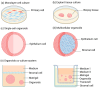
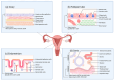
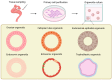
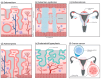
The female reproductive tract (FRT) serves as the core of human reproduction, and its health is directly related to population quantity and family happiness. The high incidence rate of female reproductive tract diseases globally poses a severe threat to women's health. Nevertheless, the exploration of its physiological functions and pathological mechanisms still lacks satisfactory research models. Organoids, as an emerging technology, not only circumvent numerous ethical issues existing in in vivo experiments but also precisely replicate the morphological structure and characteristics of the simulated tissues. The purpose of this article is to summarize the basic paradigms of organoid establishment and their applications in female reproductive research. Specifically, this article summarizes the cell sources, extracellular scaffolds, and culture media used in the establishment of organoids. It also describes the applications and future development prospects of female reproductive tract organoids established in current research in physiological and pathological studies. The importance of organoid technology in the female reproductive tract research cannot be ignored. It has opened up new avenues for research in this field and greatly promoted the exploration of female reproductive health and disease mechanisms.
Keywords: female reproductive tract; hydrogel; organoid; reproductive disorder; reproductive physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethical considerations for advancing research using organoid models derived from the placenta.Hum Reprod Update. 2025 Jul 1;31(4):392-401. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmaf007. Hum Reprod Update. 2025. PMID: 40096642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organoid Models Established from Primary Tumors and Patient-Derived Xenograft Tumors Reflect Platinum Sensitivity of Ovarian Cancer Patients.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 2:2024.06.28.601283. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.28.601283. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654830 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Vascularised organoids: Recent advances and applications in cancer research.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70258. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70258. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40045486 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo oxygen, temperature and pH dynamics in the female reproductive tract and their importance in human conception: a systematic review.Hum Reprod Update. 2018 Jan 1;24(1):15-34. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmx028. Hum Reprod Update. 2018. PMID: 29077897
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

