β-Secosterol, an Oxyphytosterol Produced Through the Reaction of β-Sitosterol with Ozone, Demonstrates Different Cytotoxic Effects on BRL-3A and HTC Cells
- PMID: 40723811
- PMCID: PMC12292371
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15070939
β-Secosterol, an Oxyphytosterol Produced Through the Reaction of β-Sitosterol with Ozone, Demonstrates Different Cytotoxic Effects on BRL-3A and HTC Cells
Abstract
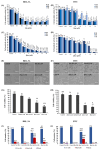
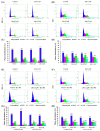
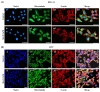
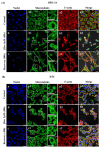
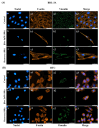
Sitosterol (Sito) is a phytosterol with bioactive properties, including reducing atherosclerosis risk and anti-inflammatory and antitumoral effects. However, it can be oxidized by reactive oxygen species such as ozone (O3), producing oxyphytosterols with harmful effects such as cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and proatherogenicity. Ozone, a strong oxidant and common pollutant, can alter plant steroid compounds, raising concerns about dietary oxyphytosterol intake. Studies identify β-Secosterol (βSec) as the primary ozone-derived oxyphytosterol from Sito, exhibiting cytotoxic effects on HepG2 human liver tumor cells. This study investigated βSec's biological effects on two rat liver cell lines: BRL-3A (immortalized) and HTC (tumoral), examining cell death, cell cycle progression, morphology, and cytoskeleton organization. While Sito influenced cell metabolic activity without affecting cell survival or morphology, βSec demonstrated significant cytotoxicity in both cell lines. It induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and disrupted cytoskeleton organization, with different implications: BRL-3A cells showed persistent cytoskeletal changes potentially linked to tumor induction, while HTC cells displayed chemoresistance, restoring cytoskeletal integrity and enhancing metastatic potential. These findings reveal βSec's complex, context-dependent effects, suggesting it may promote tumor-like behavior in non-tumoral cells and resistance mechanisms in cancer cells, contributing to understanding oxyphytosterols' implications for physiological and pathological conditions.
Keywords: cell cycle; cytoskeleton; oxyphytosterols; ozone; sitosterol; β-secosterol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
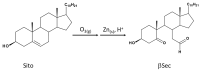
Similar articles
-
Biological effects of an oxyphytosterol generated by β-Sitosterol ozonization.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Dec 15;696:108654. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108654. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 33130087
-
Characterization of oxyphytosterols generated by β-sitosterol ozonization.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Aug 15;689:108472. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108472. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32590065
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Liang Y.T., Wong W.T., Guan L., Tian X.Y., Ma K.Y., Huang Y., Chen Z.-Y. Effect of Phytosterols and Their Oxidation Products on Lipoprotein Profiles and Vascular Function in Hamster Fed a High Cholesterol Diet. Atherosclerosis. 2011;219:124–133. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.06.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2015/17177-6/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2014/14801-8/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2019/19506-8/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 316504/2021/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 440472/2022-91/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

