Integrated Multi-Omics of the Longissimus Dorsal Muscle Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveals Intramuscular Fat Accumulation Mechanism with Diet Energy Differences in Yaks
- PMID: 40723897
- PMCID: PMC12292755
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15071025
Integrated Multi-Omics of the Longissimus Dorsal Muscle Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveals Intramuscular Fat Accumulation Mechanism with Diet Energy Differences in Yaks
Abstract
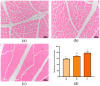
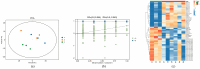
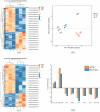
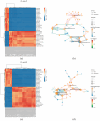
IMF (intramuscular fat, IMF), as a key index for evaluating meat quality traits (shear force and cooking loss, etc.), and its deposition process are jointly regulated by nutritional and genetic factors. In this study, we analyzed the molecular regulation mechanism of IMF deposition in the LD (longissimus dorsal muscle, LD) by dietary energy level in Pamir yaks. Meat quality assessment showed that the meat quality of the High-energy diet group (1.53 MJ/Kg, G) and the Medium-energy diet group (1.38 MJ/Kg, Z) were significantly improved compared with that of the Low-energy diet group (0.75 MJ/Kg, C), in which IMF content in the LD of yaks in G group was significantly higher (p < 0.05) compared with Z and C groups. Further analysis by combined transcriptomics and lipid metabolomics revealed that the differences in IMF deposition mainly originated from the metabolism of lipids, such as TG (triglycerides, TG), PS (phosphatidylserine, PS), and LPC (lysophosphatidylcholine, LPC), and were influenced by SFRP4, FABP4, GADD45A, PDGFRA, RBP4, and DGAT2 genes, further confirming the importance of lipid-gene interactions in IMF deposition. This study reveals the energy-dependent epigenetic regulatory mechanism of IMF deposition in plateau ruminants, which provides molecular targets for optimizing yak nutritional strategies and quality meat production, while having important theoretical and practical value for the sustainable development of livestock husbandry on the Tibetan Plateau.
Keywords: intramuscular fat deposition; lipid metabolomics; longissimus dorsal muscle; transcriptomics; yak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alternative polyadenylation landscape of longissimus dorsi muscle with high and low intramuscular fat content in cattle.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae357. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae357. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39565284
-
Evaluation of the residual feed intake on carcass and meat quality traits of Nellore bulls: a biochemical and molecular approach.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf148. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf148. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40322911
-
Research advances in intramuscular fat deposition and chicken meat quality: genetics and nutrition.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 16;16(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01234-5. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40665461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bivariate GWAS performed on rabbits divergently selected for intramuscular fat content reveals pleiotropic genomic regions and genes related to meat and carcass quality traits.Genet Sel Evol. 2025 Jul 11;57(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12711-025-00971-5. Genet Sel Evol. 2025. PMID: 40646437 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Y., Zong W., Zhao S., Qie M., Yang X., Zhao Y. Nutrition and edible characteristics, origin traceability and authenticity identification of yak meat and milk: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023;139:104133. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2023.104133. - DOI
-
- Bao P.J., Ding Z.Q., Ma X.M., La Y.F., Guo T., Zheng X.B., Ma J.E.D., Dao M., Zhou C., Zuo E.W., et al. Study on Slaughter Performance and Meat Quality of Pamir Yak. China Herbiv. Sci. 2024;44:83–87.
-
- Zhong J.C., Wang H., Chai Z.X., Ma Z.J. Exploitation and innovative utilization of yak germplasm resources. Chin. Livest. Poult. Breed. 2022;18:22–29.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

