β-Catenin: A Key Molecule in Osteoblast Differentiation
- PMID: 40723914
- PMCID: PMC12293748
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15071043
β-Catenin: A Key Molecule in Osteoblast Differentiation
Abstract
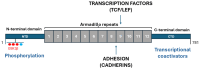
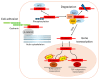
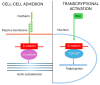
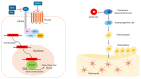
β-catenin is a key regulator of osteoblast differentiation, proliferation, and bone homeostasis. Through its interaction with transcription factors such as TCF/LEF, Runx2, and Osx, it coordinates gene expression essential for osteogenesis. The aim of this review is to demonstrate how β-catenin signaling is modulated by various physiological and pathological factors, including mechanical loading, oxidative stress, HIV-1 gp120, fluoride, implant topography, and microRNAs. These factors influence Wnt/β-catenin signaling through different mechanisms, often exerting opposing effects on osteoblast function. By integrating these modulators, we provide a comprehensive view of the dynamic regulation of β-catenin in bone biology. Understanding this complexity may provide insight into novel therapeutic strategies targeting β-catenin in bone regeneration, metabolic bone diseases, and pathologies such as HIV-associated bone loss or osteosarcoma.
Keywords: Wnt signaling; bone; differentiation of osteoblasts; osteoblasts; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

