Personalised Nutrition Approaches in the Prevention and Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review of Evidence and Practice
- PMID: 40724114
- PMCID: PMC12294222
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph22071047
Personalised Nutrition Approaches in the Prevention and Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review of Evidence and Practice
Abstract
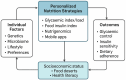
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remains a significant global public health concern, largely driven by poor dietary habits, physical inactivity, and rising obesity rates. In recent years, personalised nutrition (PN) emerged as a promising approach to T2DM prevention and management. This narrative review synthesises current evidence on tailored dietary strategies, including the glycaemic index (GI), glycaemic load (GL), food insulin index (FII), and precision nutrition tools. It further explores their impact on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and adherence to dietary interventions. A structured review of peer-reviewed and grey literature was conducted, taking into account behavioural, cultural, and systemic implementation factors. Although evidence supports the efficacy of PN in improving metabolic outcomes, implementation in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) remains limited due to infrastructural, financial, and contextual challenges. This review emphasises the need for context-specific, scalable solutions integrated into primary healthcare systems.
Keywords: dietary intervention; food insulin index; glycaemic control; glycaemic index; glycaemic load; personalised nutrition; precision nutrition; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Diabetes Atlas, 11th Edition. 2025. [(accessed on 20 April 2025)]. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/idf-diabetes-atlas-2025/?mc_cid=b5d3....
-
- Minari T.P., Tácito L.H.B., Yugar L.B.T., Ferreira-Melo S.E., Manzano C.F., Pires A.C., Moreno H., Vilela-Martin J.F., Cosenso-Martin L.N., Yugar-Toledo J.C. Nutritional strategies for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A narrative review. Nutrients. 2023;15:5096. doi: 10.3390/nu15245096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical