Ex-Vapers' Perspectives on Helpful and Unhelpful Influences During Their Quit Journeys
- PMID: 40724139
- PMCID: PMC12294330
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph22071073
Ex-Vapers' Perspectives on Helpful and Unhelpful Influences During Their Quit Journeys
Abstract
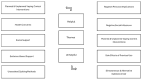
There is limited understanding of what influences vaping cessation, especially as vaping regulations change, and different jurisdictions have different regulations. This study involves 281 ex-vapers (16-24 years) from Nova Scotia, Canada. A content analysis was used to understand and compare youth and young adults' (YA) experiences of quitting vaping. Both helpful and unhelpful factors for quitting vaping were identified; each category had five themes and twenty-one sub-themes. Helpful factors were consistent across both age categories and included planned and unplanned vaping control interventions, health concerns, social support, evidence-based support, and unassisted quitting methods. Similarly, the five themes identified as unhelpful factors were consistent for both age groups: negative personal implications, negative social influences, planned and unplanned vaping control interventions, the side effects of previous use, and simultaneous and alternative substance use. Policies that limit access and raise awareness about lung health and well-being can help youth quit vaping. For YAs, increasing awareness about social support and health concerns is crucial. Raising e-cigarette costs and reducing vaping normalization supports quitting for YAs. Stress reduction and training to handle social pressure could aid youth, while YAs might benefit from treatment for other substance use to help with nicotine quitting.
Keywords: ex-vapers; policy change; quitting behaviors; vaping cessation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Salafia C.C., DiPlacido J. Social media and vaping in college students: The role of social norms and motives. J. Soc. Media Soc. 2022;11:3–26.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical