Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Soluble and Insoluble Dietary Fibers in Whole Grains and Their Health Benefits
- PMID: 40724270
- PMCID: PMC12295008
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14142447
Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Soluble and Insoluble Dietary Fibers in Whole Grains and Their Health Benefits
Abstract
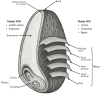
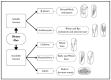
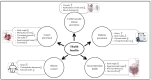
The growing global prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is drawing an increasing amount of attention to the health-promoting potential of whole-grain dietary fibers. Whole grains are rich sources of both soluble dietary fiber (SDF) and insoluble dietary fiber (IDF), contributing distinct physicochemical properties and playing vital roles in promoting human health. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the dietary fiber compositions of various whole grains, including wheat, oats, barley, rye, corn, sorghum, and rice, highlighting their structural characteristics, physiochemical properties, and associated health benefits. The physicochemical properties of dietary fibers, such as solubility, water- and oil-holding capacity, viscosity, swelling ability, and bile-acid-binding capacity, contribute significantly to their technological applications and potential health benefits, particularly in the prevention of NCDs. Although there is growing evidence supporting their health benefits, global whole-grain intake remains below recommended levels. Therefore, promoting whole-grain intake and developing fiber-rich functional foods are essential for enhancing public health and preventing chronic diseases. Future research should focus on enhancing the bioavailability and functionality of whole-grain dietary fibers, optimizing the methods by which they are extracted, and exploring their potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Keywords: dietary fiber; non-communicable diseases; physicochemical properties; whole grains.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gluten-Associated Medical Problems.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30860740 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Should Grain-Based Staple Foods Be Included in Admonitions to "Avoid Processed and Ultra-Processed Food"?Nutrients. 2025 Jun 30;17(13):2188. doi: 10.3390/nu17132188. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40647292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Effects of a fiber-degrading enzyme on ileal digestibility of amino acids and fiber and total tract digestibility of energy and fiber in growing pigs fed diets with high level of corn distillers grains with solubles.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf076. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf076. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40096523
References
-
- Zhang S., Xu X., Cao X., Liu T. The Structural Characteristics of Dietary Fibers from Tremella Fuciformis and Their Hypolipidemic Effects in Mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2023;12:503–511. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.052. - DOI
-
- European Commission Whole Grain. Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Knowledge Gateway. [(accessed on 14 November 2023)]. Available online: https://knowledge4policy.ec.europa.eu/health-promotion-knowledge-gateway....
-
- Micha R., Khatibzadeh S., Shi P., Andrews K.G., Engell R.E., Mozaffarian D. Global, Regional and National Consumption of Major Food Groups in 1990 and 2010: A Systematic Analysis Including 266 Country-Specific Nutrition Surveys Worldwide. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e008705. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources