Decoding the Molecular Mechanisms of Menthol Isomer Perception Based on Computational Simulations
- PMID: 40724312
- PMCID: PMC12294335
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14142494
Decoding the Molecular Mechanisms of Menthol Isomer Perception Based on Computational Simulations
Abstract
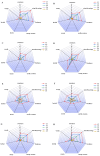
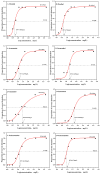
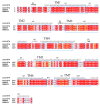
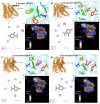
The flavor characteristics, perception, and molecular mechanisms of eight menthol isomers were investigated by sensory analysis combined with computational simulations. The sensory analysis results show significant differences in the odor profiles of the different menthol isomers. Among them, L-menthol shows a pleasant, sweet, and mint-like odor with a distinct freshness and no off-flavors, whereas the remaining seven isomers were interspersed with negative odors (musty, herbal, or earthy aromas). L-menthol and D-menthol had the lowest detection thresholds of 5.166 and 4.734 mg/L, respectively. The molecular docking results of the menthol isomers with olfactory receptors (Olfr874, OR8B8, and OR8B12) indicate that hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions were the key binding forces. The binding energy ranged from -7.3 to -5.1 kcal/mol. Residues His-55 (Olfr874), Thr-56 (Olfr874), Leu-55 (OR8B8), Tyr-94 (OR8B8), Thr-57 (OR8B8), Phe-199 (OR8B12), and Ser-248 (OR8B12) with high frequencies particularly contributed to the recognition of menthol isomers. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of the olfactory perception mechanism of menthol and provide data support for the development and precise application of minty odorants.
Keywords: detection threshold; isomers; menthol; molecular docking; sensory evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Knowledge and Use of Menthol-Mimicking Cigarettes Among Adults in the US.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Jan 2;8(1):e2454608. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.54608. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 39808430 Free PMC article.
-
Q-learning with temporal memory to navigate turbulence.Elife. 2025 Jul 21;13:RP102906. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102906. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40690282 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing neuropathy caused by cisplatin and related compounds.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Mar 31;2014(3):CD005228. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005228.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24687190 Free PMC article.
-
Non-tobacco nicotine E-cigarette use and flavored E-cigarette use among young adults in the United States.Prev Med. 2024 Jul;184:108001. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2024.108001. Epub 2024 May 11. Prev Med. 2024. PMID: 38735588 Free PMC article.
-
Oral herbal therapies for treating osteoarthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 22;2014(5):CD002947. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002947.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24848732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casares N., Alfaro M., Cuadrado-Tejedor M., Lasarte-Cia A., Navarro F., Vivas I., Lasarte J.J. Improvement of cognitive function in wild-type and Alzheimer´s disease mouse models by the immunomodulatory properties of menthol inhalation or by depletion of T regulatory cells. Front. Immunol. 2023;14:1130044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

