Nutritional Enhancement of Crackers Through the Incorporation of By-Products from the Frozen Pumpkin Industry
- PMID: 40724369
- PMCID: PMC12294666
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14142548
Nutritional Enhancement of Crackers Through the Incorporation of By-Products from the Frozen Pumpkin Industry
Abstract
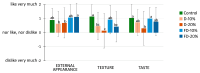
The agri-food sector faces the challenge of valorizing by-products and reducing waste. The frozen pumpkin industry generates substantial amounts of by-products rich in nutritional value, especially β-carotene. This study evaluates the nutritional and physical impact of incorporating pumpkin pulp flour (dehydrated and freeze-dried) obtained from by-products into cracker formulation. Crackers were prepared by replacing 10% and 20% of wheat flour with pumpkin flour, assessing the effects based on drying method. Physical parameters (expansion, color, and texture parameters) were measured, in the dough and in the baked products. Furthermore, β-carotene content was analyzed by HPLC-DAD, antioxidant capacity was measured with DPPH, ABTS, and ORAC, and total phenolic content was evaluated with the Folin-Ciocalteu method. Proximate composition and mineral content were also analyzed. Additionally, a preliminary sensory evaluation was conducted with 50 untrained consumer judges to assess acceptability of external appearance, texture, and taste. The inclusion of pumpkin flour significantly increased β-carotene content (up to 2.36 mg/100 g), total phenolics, and antioxidant activity of the baked crackers. Proximate analysis showed a marked improvement in fiber content and a slight reduction in energy value compared to wheat flour. Mineral analysis revealed that pumpkin flours exhibited significantly higher levels of K, Ca, Mg, and P, with improved but not always statistically significant retention in the final crackers. Freeze-dried flour retained more bioactive compounds and enhanced color. However, it also increased cracker hardness, particularly with dehydrated flour. Only the 10% freeze-dried formulation showed mechanical properties similar to those of the control. Sensory analysis indicated that all formulations were positively accepted, with the 10% freeze-dried sample showing the best balance in consumer preference across all evaluated attributes. Frozen pumpkin by-products can be effectively valorized through their incorporation into bakery products such as crackers, enhancing their nutritional and functional profile. Freeze-drying better preserves antioxidants and β-carotene, while a 10% substitution offers a balance between nutritional enrichment and technological performance and sensory acceptability.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; cracker reformulation; functional foods; pumpkin pulp flour; valorization of by-products; β-carotene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Although Irene Garcia Panadero is affiliated with JNG-BIO, her contribution to this work was strictly scientific and did not involve any financial or commercial interest. No part of the study was influenced by commercial considerations, and the results presented are entirely independent and objective. The company did not sponsor the research, and there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Use of Whey Powder to Improve Bread Quality: A Sustainable Solution for Utilizing Dairy By-Products.Foods. 2025 Aug 21;14(16):2911. doi: 10.3390/foods14162911. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40870823 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential Use of Protein From Pumpkin and Spinach Leaves for Dough Fortification: A Comprehensive Investigation Into Dough Rheology and Nutritional Benefits.J Food Sci. 2025 Aug;90(8):e70455. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70455. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40785487
-
Enhancing the Quality and Nutritional Properties of Gluten-Free Pancakes Using Sprouted Quinoa Flour Treated With Magnetic Fields, Ultrasound, and Infrared Drying.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 18;13(7):e70502. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70502. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40688604 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nakagawa K., Kono S. Food Freezing. In: Jacob-Lopes E., Queiroz Zepka L., Costa Deprá M., editors. Smart Food Industry: The Blockchain for Sustainable Engineering: Fundamentals, Technologies, and Management. Volume 1. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2023. pp. 149–167.
-
- Kitinoja L. Use of cold chains for reducing food losses in developing countries. Population. 2013;6:5–60.
-
- Rațu R.N., Veleșcu I.D., Stoica F., Usturoi A., Arsenoaia V.N., Crivei I.C., Postolache A.N., Lipșa F.D., Filipov F., Florea A.M. Application of agri-food by-products in the food industry. Agriculture. 2023;13:1559. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13081559. - DOI
-
- Pimentel-Moral S., de la Luz Cádiz-Gurrea M., Rodríguez-Pérez C., Segura-Carretero A. Recent advances in extraction technologies of phytochemicals applied for the revaluation of agri-food by-products. In: Prakash A., editor. Functional and Preservative Properties of Phytochemicals. Academic Press; London, UK: 2020. pp. 209–239.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

