The Association of Histological Signs of Plaque Instability with Low eGFR, Higher Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Lower Serum MCP-1 Levels in Carotid Endarterectomy Patients-A Single-Center, Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 40724511
- PMCID: PMC12298409
- DOI: 10.3390/life15071008
The Association of Histological Signs of Plaque Instability with Low eGFR, Higher Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Lower Serum MCP-1 Levels in Carotid Endarterectomy Patients-A Single-Center, Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
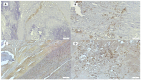
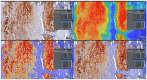
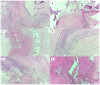
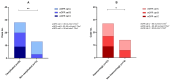
Background: Histological signs of carotid atheromatous plaque vulnerability, such as hemorrhage, neovascularization, atherothrombosis, and ulceration, develop against an unstable biological background. Declining renal function contributes to atherosclerotic progression and worsens cardiovascular outcomes. Methods: In a single-center prospective cohort study, we studied 41 endarterectomized patients with severe carotid atherosclerosis. The histological samples were stained with H&E to assess morphology and immunohistochemically labeled with antibodies for CRP and MMP-9 proteins. Complete blood count, the presence of serum biomarkers hsCRP, oxLDL, MCP-1, and MMP-9, and the level of eGFR were determined. Results: Twenty-eight patients with complicated plaques had significantly lower eGFR values: 79.5 (24-110) vs. 94 (69-114) (p = 0.004). Patients with eGFR > 90 mL/min/1.73m2 had a higher incidence of intraplaque hemorrhage and histologic complications of any cause (p = 0.012 and p = 0.003). Patients with bleeding and ulceration from the carotid plaque had a higher neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. Significantly lower levels of MCP-1 were found in the serum of patients with massive inflammatory infiltrate of the carotid plaques, while serum levels of biomarkers like hsCRP, MMP-9, and oxLDL did not show differences in cases with plaque vulnerability. Conclusions: Signs of plaque vulnerability are associated with reduced renal function, a higher neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, and lower serum levels of MCP-1 in advanced carotid artery stenosis disease.
Keywords: biomarkers; carotid stenosis; eGFR; endarterectomy; intraplaque hemorrhage; plaque vulnerability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood Flow Turbulence Measured by High-frame-rate Vector Flow Imaging Conduced to Investigating Advanced Carotid Plaque Vulnerability.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025 Jul 14:S0301-5629(25)00189-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2025.05.034. Online ahead of print. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40664546
-
Carotid Artery Surgery.2025 May 2. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 May 2. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28722976 Free Books & Documents.
-
FGF-23 as a Biomarker for Carotid Plaque Vulnerability: A Systematic Review.Med Sci (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;13(1):27. doi: 10.3390/medsci13010027. Med Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137447 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Admission Glucose and Inflammatory Markers in Histopathological Features of Atherosclerotic Plaques in Carotid and Femoro-Popliteal Arteries.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 May 12;61(5):879. doi: 10.3390/medicina61050879. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40428837 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Characteristics of Symptomatic Carotid Plaques: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;40(3-4):165-74. doi: 10.1159/000437339. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26279159
References
-
- Anbar R., Sultan S.R., Saikhan L.A., Alkharaiji M., Chaturvedi N., Hardy R., Richards M., Hughes A. Is carotid artery atherosclerosis associated with poor cognitive function assessed using the Mini-Mental State Examination? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e055131. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055131. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

