DNA Methylation: A Key Regulator in Male and Female Reproductive Outcomes
- PMID: 40724612
- PMCID: PMC12298693
- DOI: 10.3390/life15071109
DNA Methylation: A Key Regulator in Male and Female Reproductive Outcomes
Abstract
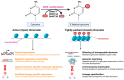
DNA methylation is a well-studied epigenetic modification that regulates gene expression, maintains genome integrity, and influences cell fate. It is strictly regulated by a group of enzymes known as DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). Most DNA methylation occurs at cytosines within symmetrical CpG dinucleotide base pairs, often located at gene promoters or other regulatory elements. Thus, methylation of a promoter CpG island leads to stable transcriptional repression of the associated gene. Nonetheless, abnormal gene expression caused by alterations in DNA methylation has been linked to infertility in both males and females, as well as to reproductive potential and improper post-fertilization embryo development. Recent epigenetic advancements have highlighted the significant association between epigenetic modification and reproductive health outcomes, garnering considerable attention. In this review, we explore significant advancements in understanding DNA methylation, emphasizing its establishment, maintenance, and functions in male and female reproductive sex cells. We also shed light on the recent discoveries on the influence of environmental exposures, nutrition, infection, stress, and lifestyle choices on DNA methylation. Finally, we discuss the latest insights and future directions concerning the diverse functions of DNA methylation in reproductive outcomes.
Keywords: DNA methylation; age; epigenetic modification; infection; lifestyle; obesity; reproductive health; steroids; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

