Burnout Syndrome Among Spanish Professionals Dedicated to Implant Dentistry: An Observational Study
- PMID: 40724749
- PMCID: PMC12294223
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13141724
Burnout Syndrome Among Spanish Professionals Dedicated to Implant Dentistry: An Observational Study
Abstract
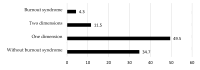
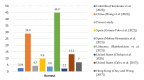
Background: Burnout syndrome (BS) is an occupational condition resulting from chronic stress, characterized by three dimensions, emotional exhaustion (EE), depersonalization (DE), and diminished personal accomplishment (PA), particularly prevalent in caregiving professions such as healthcare. The aim of this study is to analyse the prevalence of BS among Spanish dental implantology specialists, along with the impact of demographic, educational, and professional aspects. Methods: This is a cross-sectional observational study based on the STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) guidelines and was open to respondents from May to December 2024. An electronic survey based on the Maslach Burnout Inventory-Human Services Survey (MBI-HSS) was sent to members of the Spanish Society of Implants. The data were analysed using descriptive analysis. Results: A total of 305 participants (20.9%) (31.5% females and 68.5% males) completed the questionnaire. The prevalence of BS was 4.3%; however, 61.0% of the dentists showed signs of suffering from the syndrome. The mean values of EE were "average" (20.3 ± 13.8) and of DE and EE "low" (5.1 ± 5.9, and 32.5 ± 14.5, respectively). The factors significantly associated with suffering from BS were being female and having more than 20 years of experience in dental implant treatments. Conclusions: It is advisable to conduct instructive and awareness-raising initiatives among dental professionals to promote an awareness of their mental health, ultimately aiming at preserving their physical and emotional well-being while delivering optimal care to their patients.
Keywords: Maslach burnout inventory; burnout, professional; burnout, psychological; caregiver burden; dental implants; surveys and questionnaires.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suicidal Ideation, Lifestyle Factors, and Burnout Syndrome Among Spanish Professionals in Implant Dentistry: A Survey-Based Cross-Sectional Observational Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 4;14(15):5486. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155486. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40807105 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of burnout syndrome among anesthesiologists, anesthesia technicians, and intensive care unit nurses in Palestinian hospitals: a cross-sectional study.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 28;24(1):740. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06196-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39468477 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of burnout in health professionals working in palliative care: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2017 Jul;15(7):1905-1933. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003309. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2017. PMID: 28708752
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Individual-level interventions for reducing occupational stress in healthcare workers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 12;5(5):CD002892. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002892.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37169364 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Suicidal Ideation, Lifestyle Factors, and Burnout Syndrome Among Spanish Professionals in Implant Dentistry: A Survey-Based Cross-Sectional Observational Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 4;14(15):5486. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155486. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40807105 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

