Assessing Occupational Work-Related Stress and Anxiety of Healthcare Staff During COVID-19 Using Fuzzy Natural Language-Based Association Rule Mining
- PMID: 40724770
- PMCID: PMC12294843
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13141745
Assessing Occupational Work-Related Stress and Anxiety of Healthcare Staff During COVID-19 Using Fuzzy Natural Language-Based Association Rule Mining
Abstract
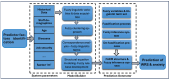
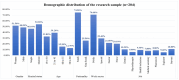
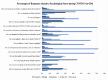
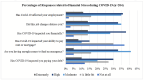
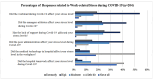
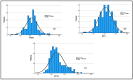
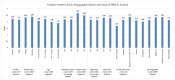
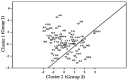
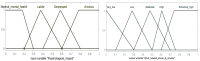
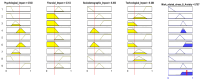
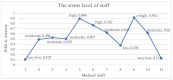
Background/Objective: Frontline healthcare staff who contend diseases and mitigate their transmission were repeatedly exposed to high-risk conditions during the COVID-19 pandemic. They were at risk of mental health issues, in particular, psychological stress, depression, anxiety, financial stress, and/or burnout. This study aimed to investigate and evaluate the occupational stress of medical doctors, nurses, pharmacists, physiotherapists, and other hospital support crew during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia. Methods: We collected both qualitative and quantitative data from a survey given to public and private hospitals using methods like correspondence analysis, cluster analysis, and structural equation models to investigate the work-related stress (WRS) and anxiety of the staff. Since health-related factors are unclear and uncertain, a fuzzy association rule mining (FARM) method was created to address these problems and find out the levels of work-related stress (WRS) and anxiety. The statistical results and K-means clustering method were used to find the best number of fuzzy rules and the level of fuzziness in clusters to create the FARM approach and to predict the work-related stress and anxiety of healthcare staff. This innovative approach allows for a more nuanced appraisal of the factors contributing to work-related stress and anxiety, ultimately enabling healthcare organizations to implement targeted interventions. By leveraging these insights, management can foster a healthier work environment that supports staff well-being and enhances overall productivity. This study also aimed to identify the relevant health factors that are the root causes of work-related stress and anxiety to facilitate better preparation and motivation of the staff for reorganizing resources and equipment. Results: The results and findings show that when the financial burden (FIN) of healthcare staff increased, WRS and anxiety increased. Similarly, a rise in psychological stress caused an increase in WRS and anxiety. The psychological impact (PCG) ratio and financial impact (FIN) were the most influential factors for the staff's anxiety. The FARM results and findings revealed that improving the financial situation of healthcare staff alone was not sufficient during the COVID-19 pandemic. Conclusions: This study found that while the impact of PCG was significant, its combined effect with FIN was more influential on staff's work-related stress and anxiety. This difference was due to the mutual effects of PCG and FIN on the staff's motivation. The findings will help healthcare managers make decisions to reduce or eliminate the WRS and anxiety experienced by healthcare staff in the future.
Keywords: burnout; depression; fuzzy association rule mining; mental health; occupational stress; resilience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
A model of occupational stress to assess impact of COVID-19 on critical care and redeployed nurses: a mixed-methods study.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024 Dec;13(23):1-32. doi: 10.3310/PWRT8714. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024. PMID: 39708055
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Technology-enabled CONTACT tracing in care homes in the COVID-19 pandemic: the CONTACT non-randomised mixed-methods feasibility study.Health Technol Assess. 2025 May;29(24):1-24. doi: 10.3310/UHDN6497. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40350743 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that influence the provision of intrapartum and postnatal care by skilled birth attendants in low- and middle-income countries: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 17;11(11):CD011558. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011558.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29148566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chung H.J., Kim M.H., Ahn S., Yeo J., Lee K., Kim S., Kang S., Suh W. Development of the Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics-9 (SAVE-9) Scale for Assessing Work-related Stress and Anxiety in Healthcare Personnel in Response to Viral Epidemics. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021;36:47. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2023. [(accessed on 25 May 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int.
-
- Adiguzel O. The Effect of Work-Related Stress, Role Conflict and Role Ambiguity on Expected Turnover. Appl. Nurses. 2012;8:49.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

