Vitamin D Reshapes Genomic Hierarchies in Skin Cells: lncRNA-Driven Responses in Carcinoma Versus Transcription Factor-Based Regulation in Healthy Skin
- PMID: 40724881
- PMCID: PMC12296165
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146632
Vitamin D Reshapes Genomic Hierarchies in Skin Cells: lncRNA-Driven Responses in Carcinoma Versus Transcription Factor-Based Regulation in Healthy Skin
Abstract
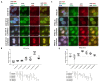
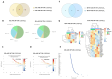
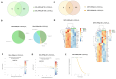
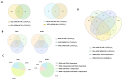
The active form of vitamin D3, 1,25(OH)2D3, exerts hierarchical control over gene expression, initially targeting transcription factors (TFs) that drive downstream responses. Here, we profile the transcriptional landscape of primary keratinocytes (HPEKp) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells in response to 1,25(OH)2D3, revealing a distinct shift in regulatory targets. While TFs accounted for 9.23% of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in keratinocytes, this proportion dropped to 4.9% with prolonged exposure. In contrast, SCC cells displayed a five-fold reduction in TFs deregulation and a concurrent enrichment of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), which comprised 22.25% of DEGs after 24 h treatment, with 81% upregulated. Integrative transcriptomic and in silico analyses showed that lncRNA induction was predominantly VDR-dependent, partially RXRA-dependent, and PDIA3-independent. Notably, 90% of deregulated lncRNAs were atypical for head and neck SCC. Several of these lncRNAs exhibit potential antitumor properties and may modulate SCC cell responsiveness to interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). In conclusion, these findings suggest that in SCC cells, the regulation of lncRNA expression-rather than transcription factor modulation-may represent a mechanism of the cellular response to 1,25(OH)2D3.
Keywords: long non-coding RNAs; squamous cell carcinoma; vitamin D3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The vitamin D3 hormone, 1,25(OH)2D3, regulates fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) production in human skin cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Apr 1;328(4):C1177-C1192. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00827.2024. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40055144 Free PMC article.
-
p62 mRNA suppresses NLRP1 expression in cutaneous SCC cells through miR-34a-5p.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):465. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07785-9. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40593496 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 increases invasion of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-associated cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by modifying transforming growth factor-β signalling.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Dec 23;192(1):104-117. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae295. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39018437 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;810:69-105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0437-2_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25207361
-
New Approaches to Assess Mechanisms of Action of Selective Vitamin D Analogues.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 16;22(22):12352. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212352. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

