Overexpression of Circular PRMT1 Transcripts in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Predicts Recurrence and Poor Overall Survival
- PMID: 40724932
- PMCID: PMC12294339
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146683
Overexpression of Circular PRMT1 Transcripts in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Predicts Recurrence and Poor Overall Survival
Abstract
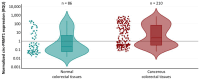
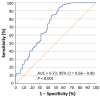
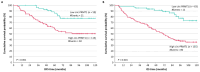
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most prevalent and deadly neoplasms globally; this fact puts emphasis on the need for accurate molecular biomarkers for early detection and accurate prognosis. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have recently emerged as very promising cancer biomarkers. In this study, we thoroughly examined whether the expression levels of circular transcripts of the protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) gene can predict the prognosis of patients diagnosed with colorectal adenocarcinoma, the most frequent type of CRC. Hence, a highly sensitive quantitative PCR (qPCR) assay was developed and applied to quantify circ-PRMT1 expression in cDNAs from 210 primary colorectal adenocarcinoma tissue specimens and 86 paired normal colorectal mucosae. Extensive biostatistical analysis was then performed to assess the potential prognostic power of circ-PRMT1. Significant overexpression of this molecule was observed in colorectal adenocarcinoma tissue samples in contrast to their non-cancerous counterparts. Moreover, higher circ-PRMT1 expression was correlated with poorer disease-free survival (DFS) and worse overall survival (OS) in colorectal adenocarcinoma patients. Interestingly, multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that the prognostic value of the expression of this circRNA does not depend on other established prognostic factors included in the prognostic model. Furthermore, the stratification of patients based on TNM staging revealed that higher circ-PRMT1 levels were significantly related to shorter DFS and OS intervals, particularly in patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma of TNM stage II or III. In summary, this original research study provides evidence that circ-PRMT1 overexpression represents a promising molecular biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma, not depending on other established prognostic factors such as TNM staging.
Keywords: circular RNA (circRNA); colon cancer; molecular tumor markers; non-coding RNA; prognosis; prognostic biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genetic variation in microRNA-binding site and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Jan;141(1):35-41. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1780-6. Epub 2014 Jul 31. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25079514 Free PMC article.
-
The challenge of molecular selection in liver-limited metastatic colorectal cancer for surgical resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis in the context of current and future approaches.Oncol Res. 2024 Aug 23;32(9):1407-1422. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.049181. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39220128 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour deposit count is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer-a population-based cohort study.Br J Surg. 2024 Dec 24;112(1):znae309. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znae309. Br J Surg. 2024. PMID: 39787029 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathologic significance and prognostic value of circRNAs in osteosarcoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Oct 7;16(1):578. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02568-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34620208 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Argiles G., Tabernero J., Labianca R., Hochhauser D., Salazar R., Iveson T., Laurent-Puig P., Quirke P., Yoshino T., Taieb J., et al. Localised colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020;31:1291–1305. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cervantes A., Adam R., Rosello S., Arnold D., Normanno N., Taieb J., Seligmann J., De Baere T., Osterlund P., Yoshino T., et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023;34:10–32. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

