Long-Chain Fatty Acids Alter Estrogen Receptor Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 40724972
- PMCID: PMC12294802
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146722
Long-Chain Fatty Acids Alter Estrogen Receptor Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
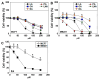
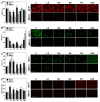
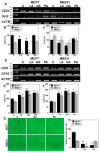
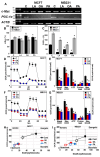
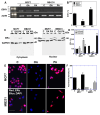
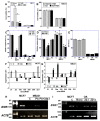
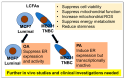
Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) have emerged as important regulators of cancer metabolism, but their impact on hormone receptor expression in breast cancer (BCA) remains poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the effects of five LCFAs-linoleic acid (LA), oleic acid (OA), elaidic acid (EA), palmitic acid (PA), and α-linolenic acid (LNA)-on two BCA cell lines: luminal-type MCF7 and triple-negative MDA-MB-231 (MB231). All LCFAs suppressed cell viability and mitochondrial function in a dose-dependent manner, accompanied by decreased membrane potential, increased reactive oxygen species production, and a metabolic shift. Notably, OA reduced both mRNA and nuclear protein levels of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in MCF7 cells, leading to impaired responses to estradiol and tamoxifen. In contrast, PA induced nuclear ERα expression in MB231 cells, although ER signaling remained inactive. MicroRNA profiling revealed that OA upregulated ER-suppressive miR-22 and miR-221 in MCF7, while PA increased miR-34a in MB231, contributing to ERα induction. These findings suggest that specific LCFAs modulate ER expression through epigenetic and post-transcriptional mechanisms, altering hormonal responsiveness in BCA. Our results offer new insights into how dietary lipids may influence therapeutic efficacy and tumor behavior by regulating nuclear receptor signaling.
Keywords: breast cancer; estrogen receptor; long-chain fatty acid; triple negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Prat A., Cheang M.C., Martín M., Parker J.S., Carrasco E., Caballero R., Tyldesley S., Gelmon K., Bernard P.S., Nielsen T.O., et al. Prognostic significance of progesterone receptor-positive tumor cells within immunohistochemically defined luminal A breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:203–209. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.43.4134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carey L.A., Berry D.A., Cirrincione C.T., Barry W.T., Pitcher B.N., Harris L.N., Ollila D.W., Krop I.E., Henry N.L., Weckstein D.J., et al. Molecular Heterogeneity and Response to Neoadjuvant Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Targeting in CALGB 40601, a Randomized Phase III Trial of Paclitaxel Plus Trastuzumab With or Without Lapatinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016;34:542–549. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.1268. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 23K19900/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 24K14281/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 25K14462/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 23K10481/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- 21K11223/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

