The Roles of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 40724973
- PMCID: PMC12295222
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146723
The Roles of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
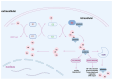
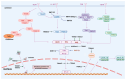
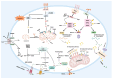
The temporary or permanent occlusion of cerebral blood vessels results in ischemic stroke (IS). Ischemia per se causes focal neuronal damage, and the subsequent ischemia-reperfusion injury that occurs after blood flow restoration further compromises brain tissue and cells in the neurovascular unit, significantly contributing to poor patient outcomes and functional impairments. Current research indicates that the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) plays a crucial role in the pathological processes associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI). Notably, E3 ubiquitin (Ub) ligases, which are essential in the UPS, have garnered increasing attention as potential novel therapeutic targets for treating ischemia-reperfusion damage in the brain. This review focuses primarily on the background of E3 Ub ligases and explores their intricate relationships with the pathological processes of CIRI.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligases; cell death; cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury; inflammation; mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

