The Dichloromethane Fraction of Sanguisorba tenuifolia Inhibits Inflammation in Cells Through Modulation of the p38/ERK/MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40724981
- PMCID: PMC12294969
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146732
The Dichloromethane Fraction of Sanguisorba tenuifolia Inhibits Inflammation in Cells Through Modulation of the p38/ERK/MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
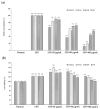
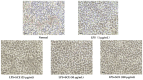
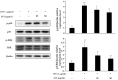
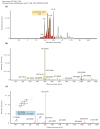
Sanguisorba tenuifolia is a wild plant of the genus Sanguisorba officinalis. This study aimed to investigate the regulatory effect of the dichloromethane fraction of Sanguisorba tenuifolia on LPS-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells, thereby providing a new scientific basis for the medicinal development of Sanguisorba tenuifolia. Initially, we used 75% ethanol to crudely extract the roots of Sanguisorba tenuifolia, followed by fractional extraction using dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), ethyl acetate (EtOAc), butanol (BuOH), and distilled water (DW) as solvents. By measuring the inhibitory effects of each fractionated extract on NO production, we determined that the SCE (Dichloromethane fraction of Sanguisorba tenuifolia) exhibited the most potent anti-inflammatory activity, leading to its progression to the next experimental stage. Subsequently, we evaluated the effects of SCE on cell viability and LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion in RAW264.7 cells. A rat model of reflux esophagitis was also used to validate the in vivo anti-inflammatory effects of SCE. Additionally, we utilized UPLC/MS-MS to identify and analyze the active components of SCE. The results indicated that SCE could effectively inhibit LPS-induced cellular inflammation by modulating the p38/ERK/MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, and also reduced the damage of the esophageal mucosa in rats with reflux esophagitis. UPLC/MS-MS analysis of SCE identified 423 compounds, including 12 active ingredients such as triterpenoids, phenols, and steroids. This discovery not only provides scientific support for the potential of Sanguisorba tenuifolia as an anti-inflammatory agent but also lays the groundwork for the development of new therapeutics for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway; Sanguisorba tenuifolia; anti-inflammatory; dichloromethane fraction.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Chang X., Zhang T., Wang J., Liu Y., Yan P., Meng Q., Yin Y., Wang S. SIRT5-Related Desuccinylation Modification Contributes to Quercetin-Induced Protection against Heart Failure and High-Glucose-Prompted Cardiomyocytes Injury through Regulation of Mitochondrial Quality Surveillance. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021;2021:5876841. doi: 10.1155/2021/5876841. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

