Regulation of Plant Genes with Exogenous RNAs
- PMID: 40725020
- PMCID: PMC12295431
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146773
Regulation of Plant Genes with Exogenous RNAs
Abstract
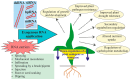
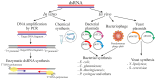
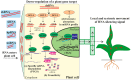
Exogenous RNA application, also known as spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS), is a new approach in plant biotechnology that utilizes RNA interference (RNAi) to modify plant traits. This technique involves applying RNA solutions of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), hairpin RNA (hpRNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), or microRNA (miRNA) directly onto plant surfaces. This triggers RNAi-mediated silencing of specific genes within the plant or invading pathogens. While extensively studied for enhancing resistance to pathogens, the application of exogenous RNA to regulate plant endogenous genes remains less explored, creating a rich area for further research. This review summarizes and analyzes the studies reporting on the exogenously induced silencing of plant endogenes and transgenes using various RNA types. We also discuss the RNA production and delivery approaches, analyze the uptake and transport of exogenous RNAs, and the mechanism of action. The analysis revealed that SIGS/exoRNAi affects the expression of plant genes, which may contribute to crop improvement and plant gene functional studies.
Keywords: RNA interference; dsRNA; exogenous RNAs; external application; gene silencing; miRNA; plant gene regulation; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

