Amine-Modified Diatomaceous Earth Syringe Platform (DeSEI) for Efficient and Cost-Effective EV Isolation
- PMID: 40725087
- PMCID: PMC12295286
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146843
Amine-Modified Diatomaceous Earth Syringe Platform (DeSEI) for Efficient and Cost-Effective EV Isolation
Abstract
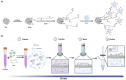
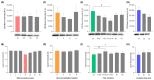
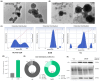
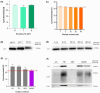
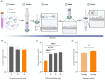
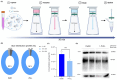
Conventional methods for isolating extracellular vesicles (EVs) are often limited by long processing times, a low purity, and a reliance on specialized equipment. To overcome these challenges, we developed the DeSEI (amine-functionalized Diatomaceous earth-based Syringe platform for EV Isolation), a novel platform employing low-cost, amine-functionalized diatomaceous earth (ADe) within a simple syringe-filter system. The capture mechanism leverages the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged ADe and the negatively charged EV surface, enabling a rapid and efficient isolation. The optimized 30 min protocol yields intact EVs with morphology, size, and protein markers comparable to those from ultracentrifugation, ensuring minimal cellular contamination. Notably, DeSEI exhibited a nearly 60-fold higher recovery efficiency of EV-derived miRNA compared to ultracentrifugation. The platform further proved its versatility with a rapid one-step miRNA extraction protocol and a user-friendly cartridge format. The direct miRNA extraction capability is particularly advantageous for a streamlined biomarker analysis, while the cartridge design illustrates a clear pathway toward developing point-of-care diagnostic tools. The DeSEI offers a promising alternative to existing methods for EV-based research by providing a combination of speed, simplicity, and procedural flexibility that does not require specialized equipment.
Keywords: EV isolation; diatomaceous earth; dimethyl sulfide; extracellular vesicle; nanomaterials; sample preparation.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Jinkwan Lee and Namheon Kim were employed by the company Infusiontech. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diverse Populations of Extracellular Vesicles with Opposite Functions during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02357-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02357-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361424 Free PMC article.
-
A practical protocol for correlative confocal fluorescence and transmission electron microscopy characterization of extracellular vesicles.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0302624. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03026-24. Epub 2025 May 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40401966 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Extracellular Vesicle Isolation: A Hybrid Electrokinetic-Tangential Flow Filtration Approach for Improved Yield, Purity, and Scalability.Anal Chem. 2025 Aug 12;97(31):16759-16768. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01168. Epub 2025 Jul 30. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40736764 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Amine-Based Photoclick Chemistry: From Concept to Diverse Applications in Chemical Biology and Medicinal Chemistry.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jul 1;58(13):1963-1981. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5c00158. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40532071 Review.
-
[Research progress of peptide recognition-guided strategies for exosome isolation and enrichment].Se Pu. 2025 May;43(5):446-454. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.10015. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40331609 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

