Nitric Oxide and Photosynthesis Interplay in Plant Interactions with Pathogens
- PMID: 40725211
- PMCID: PMC12295979
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146964
Nitric Oxide and Photosynthesis Interplay in Plant Interactions with Pathogens
Abstract
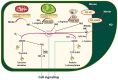
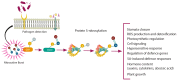
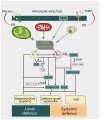
Nitric oxide and reactive nitrogen species are key signalling molecules with pleiotropic effects in plants. They are crucial elements of the redox regulation of plant stress responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. Nitric oxide is known to enhance photosynthetic efficiency under abiotic stress, and reactive nitrogen species-mediated alterations in photosynthetic metabolism have been shown to confer resistance to abiotic stresses. However, knowledge about the role of reactive nitrogen species in plant immune responses remains limited. In this review, we highlight recent advancements in understanding the role of NO in regulating stomatal movement, which contributes to resistance against pathogens. We will examine the involvement of NO in the regulation of photosynthesis, which provides energy, reducing equivalents and carbon skeletons for defence, as well as the significance of protein S-nitrosylation in relation to immune responses. The role of NO synthesis induced in pathogenic organisms during plant-pathogen interactions, along with S-nitrosylation of pathogen effectors to counteract their pathogenesis-promoting activity, is also reported. We will discuss the progress in understanding the interactions between reactive nitrogen species and photosynthetic metabolism, focusing on enhancing crop plants' productivity and resistance in challenging environmental conditions.
Keywords: S-nitrosylation; chloroplasts; immune response; infection; plant–pathogen interaction; reactive nitrogen species; stomata immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide in plant stress: Rewilding and restoring signaling for enhancing plant growth and development.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2025 Aug;1869(9):130837. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2025.130837. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2025. PMID: 40545059 Review.
-
Pattern Recognition Receptors in Plant Immunity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1476:425-451. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-85340-1_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40622553 Review.
-
Modulation of plant transcription factors and priming of stress tolerance by plant growth-promoting bacteria: a systematic review.Ann Bot. 2025 Feb 19;135(3):387-402. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcae166. Ann Bot. 2025. PMID: 39279216
-
Exploring the potential of signalling molecules hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in augmenting salt stress resilience in bitter gourd.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 1;25(1):1008. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06942-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40750854 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled nitric oxide for treating pain crises in people with sickle cell disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 8;7(7):CD011808. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011808.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35802341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mandal M., Sarkar M., Khan A., Biswas M., Masi A., Rakwal R., Agrawal G.K., Srivastava A., Sarkar A. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS) in Plants–Maintenance of Structural Individuality and Functional Blend. Adv. Redox Res. 2022;5:100039. doi: 10.1016/j.arres.2022.100039. - DOI
-
- Talaat N.B. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling in Plant Growth and Development. In: Hasanuzzaman M., Fotopoulos V., Nahar K., Fujita M., editors. Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur Species in Plants: Production, Metabolism, Signaling and Defense Mechanisms. Volume 1. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2019. pp. 225–266.
-
- Nawrocka J., Szymczak K., Maćkowiak A., Skwarek-Fadecka M., Małolepsza U. Determination of Reactive Oxygen or Nitrogen Species and Novel Volatile Organic Compounds in the Defense Responses of Tomato Plants Against Botrytis cinerea Induced by Trichoderma virens TRS 106. Cells. 2022;11:3051. doi: 10.3390/cells11193051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

