Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Based on Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin B and Evaluation of Immunological Responses in Mice
- PMID: 40725217
- PMCID: PMC12295685
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26146971
Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Based on Fasciola gigantica Cathepsin B and Evaluation of Immunological Responses in Mice
Abstract
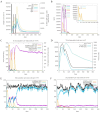
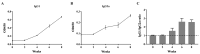
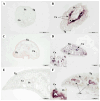
Fasciola gigantica (F. gigantica) is a vital parasite that causes fasciolosis. Liver fluke infections affect livestock animals, and the Fasciola species (Fasciola spp.) vaccine has been tested for many types of these diseases. Currently, computer-based vaccine design represents an attractive alternative for constructing vaccines. Thus, this study aimed to design the epitopes of linear B-cells (BCL) and helper T lymphocytes (HTL) using an immunoinformatic approach and to investigate in silico and the mice's immune response. A non-conserved host region, overlapping F. gigantica cathepsin B proteins (FgCatB), and the highest conserved residue percentages were the criteria used to construct epitopes. The GPGPG linker was used to link epitopes in the multi-epitope Fasciola gigantica cathepsin B (MeFgCatB) peptide. The MeFgCatB peptide has high antigenicity, non-allergenicity, non-toxicity, good solubility, and a high-quality structure. The molecular docking between the MeFgCatB peptide and Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2) was evaluated. The IgM, IgG1, and IgG2 levels were elevated in silico. In mice, the MeFgCatB peptide was synthesized and administered as an injection. The MeFgCatB-specific IgG1 and IgG2a levels were elevated after week 2, showing a predominance of IgG1. The rFgCatB1, rFgCatB2, and rFgCatB3 were detected using the MeFgCatB peptide-immunized sera. The MeFgCatB peptide-immunized sera were detected at approximately 28-34 kDa in the whole body. In addition, the MeFgCatB immunized sera can positively signal at the caecal epithelium in the NEJ, 4WKJ, and adult stages. In summary, the MeFgCatB peptide is able to induce mixed Th1/Th2 immune responses with Th2 dominating and to detect the native protein of F. gigantica. The MeFgCatB peptide should help against F. gigantica in future experiments.
Keywords: Cathepsin B; Fasciola gigantica; fasciolosis; immunoinformatic; multi-epitope; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

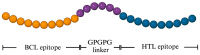



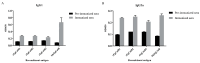

Similar articles
-
Development of multi-epitope Cathepsin L driven short peptide vaccine against Fasciola gigantica.Front Vet Sci. 2025 May 22;12:1547937. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1547937. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40475029 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine potential of recombinant cathepsin B against Fasciola gigantica.Exp Parasitol. 2013 Sep;135(1):102-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Exp Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23811052
-
Immunoinformatic design of chimeric multiepitope vaccine for the prevention of human metapneumovirus (hMPV).BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 30;25(1):964. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11339-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40739488 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics-Driven Design of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Targeting Simian Virus VP1 Major Capsid Protein for Oncogenic Viral Infection Prevention.Rev Med Virol. 2025 Sep;35(5):e70065. doi: 10.1002/rmv.70065. Rev Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 40781525 Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Mostafa W., Abdel-Rady A., El-Dakroury M.F., Felefel W. Field Trials to Evaluate Five Fasciolicides against Natural Liver Fluke Infection in Cattle and Sheep in Egypt. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2023;12:76–81. doi: 10.47278/journal.ijvs/2022.160. - DOI
-
- Tolan R.W. Fascioliasis Due to Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica Infection: An Update on This “neglected” Neglected Tropical Disease. Lab. Med. 2011;42:107–116. doi: 10.1309/LMLFBB8PW4SA0YJI. - DOI
-
- Rosas-Hostos Infantes L.R., Paredes Yataco G.A., Ortiz-Martínez Y., Mayer T., Terashima A., Franco-Paredes C., Gonzalez-Diaz E., Rodriguez-Morales A.J., Bonilla-Aldana D.K., Vargas Barahona L., et al. The Global Prevalence of Human Fascioliasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2023;10:20499361231185413. doi: 10.1177/20499361231185413. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Winaya I.B.O., Oka I.B.M., Adnyana I.B.W., Sudipa P.H. Fibrosis and Collagen-I Accumulation in Bali Cattle Liver Tissue Infected with Fasciola gigantica. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2023;12:224–229. doi: 10.47278/journal.ijvs/2022.179. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

