Identification of Molecular Subtypes of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Mexican Children by Whole-Transcriptome Analysis
- PMID: 40725249
- PMCID: PMC12295331
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26147003
Identification of Molecular Subtypes of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Mexican Children by Whole-Transcriptome Analysis
Abstract
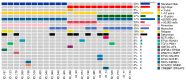
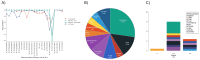
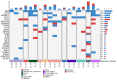
B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) is classified into more than 20 molecular subtypes, and next-generation sequencing has facilitated the identification of these with high sensitivity. Bulk RNA-seq analysis of bone marrow was realized to identify molecular subtypes in Mexican pediatric patients with B-ALL. High hyperdiploidy (27.3%) was the most frequent molecular subtype, followed by DUX4 (13.6%), TCF3::PBX1 (9.1%), ETV6::RUNX1 (9.1%), Ph-like (9.1%), ETV6::RUNX1-like (9.1%), PAX5alt (4.5%), Ph (4.5%), KMT2A (4.5%), and ZNF384 (4.5%), with one patient presenting both the PAX5alt and low hypodiploidy subtypes (4.5%). The genes TYK2, SEMA6A, FLT3, NRAS, SETD2, JAK2, NT5C2, RAG1, and SPATS2L harbor deleterious missense variants across different B-ALL molecular subtypes. The Ph-like subtype exhibited mutations in STAT2, ADGRF1, TCF3, BCR, JAK2, and NRAS with overexpression of the CRLF2 gene. The DUX4 subtype showed mutually exclusive missense variants in the PDGRFA gene. Here, we have demonstrated the importance of using RNA-seq to facilitate the differential diagnosis of B-ALL with successful detection of gene fusions and mutations. This will aid both patient risk stratification and precision medicine.
Keywords: DUX4; NGS; RNA-seq; molecular subtypes of B-ALL; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Flores-Lujano J., Duarte-Rodriguez D.A., Jimenez-Hernandez E., Martin-Trejo J.A., Allende-Lopez A., Penaloza-Gonzalez J.G., Perez-Saldivar M.L., Medina-Sanson A., Torres-Nava J.R., Solis-Labastida K.A., et al. Persistently high incidence rates of childhood acute leukemias from 2010 to 2017 in Mexico City: A population study from the MIGICCL. Front. Public Health. 2022;10:918921. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.918921. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perez-Saldivar M.L., Fajardo-Gutierrez A., Bernaldez-Rios R., Martinez-Avalos A., Medina-Sanson A., Espinosa-Hernandez L., Flores-Chapa Jde D., Amador-Sanchez R., Penaloza-Gonzalez J.G., Alvarez-Rodriguez F.J., et al. Childhood acute leukemias are frequent in Mexico City: Descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:355. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-355. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

