Solvent Fractionation of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc. for Antioxidant, Biological Activity, and Chromatographic Characterization
- PMID: 40725265
- PMCID: PMC12295684
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26147011
Solvent Fractionation of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc. for Antioxidant, Biological Activity, and Chromatographic Characterization
Abstract
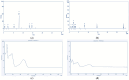
This study investigated the natural bioactive compounds in Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc. (P. cuspidatum) by fractionating a 70% ethanol extract using n-hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, and water. The total polyphenol and flavonoid contents of each fraction were determined, and their antioxidant activities were evaluated using DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays. Additionally, the anti-diabetic potential was assessed via α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, while anti-obesity activity was evaluated using lipase inhibitory activity. The fractions were also tested for tyrosinase and elastase inhibitory activities to assess their skin-whitening and anti-wrinkle potential, and their antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa was determined using the agar diffusion method. Finally, bioactive compounds were identified and quantified using HPLC and GC-MSD. The results showed that the ethyl acetate fraction possessed the highest total polyphenol content (0.53 ± 0.01 g GAE/g) and total flavonoid content (0.19 ± 0.02 g QE/g). It also exhibited strong antioxidant activity, with the lowest DPPH radical scavenging IC50 (0.01 ± 0.00 mg/mL), ABTS radical scavenging IC50 (0.06 ± 0.00 mg/mL), and the highest FRAP value (6.02 ± 0.30 mM Fe2+/mg). Moreover, it demonstrated potent enzyme inhibitory activities, including tyrosinase inhibitory activity (67.78 ± 2.50%), elastase inhibitory activity (83.84 ± 1.64%), α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (65.14 ± 10.29%), and lipase inhibitory activity (85.79 ± 1.04%). In the antibacterial activity, the ethyl acetate fraction produced a clear inhibitory zone of 19.50 mm against Staphylococcus aureus, indicating notable antibacterial activity. HPLC-PDA and GC-MSD analyses identified tannic acid and emodin as the major bioactive constituents. These findings suggest that the ethyl acetate fraction of P. cuspidatum extract, rich in polyphenol and flavonoid compounds, is a promising natural source of bioactive ingredients for applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Further research is needed to explore its mechanisms and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc.; antioxidant activity; chromatographic analyses; enzyme inhibitory activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Unveiling the ethnomedicinal potential of Alchemilla speciosa Buser: An underexplored source of bioactive compounds for skin health.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120068. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120068. Epub 2025 May 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40451493
-
Phytochemical composition and bioactivity of Debregeasia saeneb leaves: Insights into anti-diabetic and antioxidant properties.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 2;20(7):e0326991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326991. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40601679 Free PMC article.
-
Botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and potential application of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb.et Zucc.: a review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 30;148(3):729-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 May 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23707210
-
Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Activity Against MDR and Food-Borne Pathogenic Bacteria of Psidium guajava. L Fruit During Ripening.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;67(8):3070-3088. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00779-y. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 37316612
-
A systematic review on natural products with antimicrobial potential against WHO's priority pathogens.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 1;30(1):525. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02717-x. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40597250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y., Zhang T., Wang L., Liu X., Li H. Research progress on chemical constituents in roots and rhizomes of Polygonum cuspidatum and their pharmacological activities. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2016;47:3055–3063.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

