Effect of Volatile Organic Compounds from Branches of Healthy and Unhealthy Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch Trees on Host Selection by Bark Beetle Sinophloeus porteri (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
- PMID: 40725342
- PMCID: PMC12295378
- DOI: 10.3390/insects16070712
Effect of Volatile Organic Compounds from Branches of Healthy and Unhealthy Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch Trees on Host Selection by Bark Beetle Sinophloeus porteri (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
Abstract
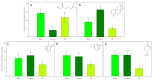
Araucaria araucana is one of the longest-living Chilean trees. Recently, Araucaria Leaf Damage disease, which causes damage to branches and crowns, was detected. Sinophloeus porteri, a bark beetle affecting A. araucana, could be associated with foliar damage. However, little is known about their ecological and chemical interactions. This study examined the olfactory response of S. porteri to volatiles emitted from A. araucana. Branches and weevils were collected from a national park, and volatiles were trapped from both healthy and unhealthy branches. Thirty terpenes were identified, some of which were reported for the first time in A. araucana. Healthy branches emitted large amounts of myrcene (>360 ng g-1 day-1), and unhealthy branches showed high hibaene emanations (>140 ng g-1 day-1). Olfactory assays verified that S. porteri was attracted to the volatile blends of branches, regardless of the health condition of the branches, but preferred the blend of unhealthy branches. Moreover, myrcene was repellent to these weevils, and hibaene acted as an attractant, suggesting that A. araucana might use myrcene for defense against S. porteri, and hibaene could stimulate host selection by beetles.
Keywords: Araucaria araucana; Sinophloeus porteri; olfactometry; volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schmithüsen J. Die Nadelhölzer in den Waldgesellschaften der südlichen Anden. Vegetatio. 1960;9:313–327. doi: 10.1007/BF02917033. - DOI
-
- Montaldo P. La Bio-Ecología de la Araucaria araucana (Mol.) Koch. Instituto Forestal Latinoamericano de Investigación y Capacitación; Mérida, Venezuela: 1974. pp. 46–48. Boletín Técnico.
-
- Gallia M.C., Bachmeier E., Ferrari A., Queralt I., Mazzeo M.A., Bongiovanni G.A. Pehuén (Araucaria araucana) seed residues are a valuable source of natural antioxidants with nutraceutical, chemoprotective and metal corrosion-inhibiting properties. Bioorganic Chem. 2020;104:104175. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104175. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nanavati W., Whitlock C., Outes V., Villarosa G. A Holocene history of monkey puzzle tree (pehuén) in northernmost Patagonia. J. Biogeogr. 2020;48:833–846. doi: 10.1111/jbi.14041. - DOI
-
- Tai X., Mackay D.S., Ewers B.E., Parsekian A.D., Baverly D., Speckman H., Brooks P.D., Anderegg P.D. Plant Hydraulic Stress Explained Tree Mortality and Tree Size Explained Beetle Attack in a Mixed Conifer Forest. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020;124:3555–3568. doi: 10.1029/2019JG005272. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

