Associations Between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Dialysis: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- PMID: 40725536
- PMCID: PMC12295821
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14144845
Associations Between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Dialysis: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
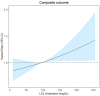
Background/Objectives: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is a causal factor in the development of atherosclerosis and a predictor of cardiovascular disease. However, the association between LDL-C levels and cardiovascular outcomes in patients undergoing dialysis remains controversial, with current guidelines advising against initiating statin therapy in this population. This study investigated the relationship between LDL-C levels and cardiovascular outcomes in Korean adults undergoing dialysis, using nationwide data. Methods: A total of 21,692 patients with end-stage kidney disease undergoing dialysis between 2009 and 2017 were identified from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. Statin non-users (primary cohort) and users (secondary cohort) comprised 15,414 and 6278 patients, respectively. LDL-C levels were categorized, and cardiovascular outcomes including composites of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and ischemic stroke were analyzed. Results: Among statin non-users, LDL-C levels > 100 mg/dL were significantly associated with an increased risk of the composite outcome, in a dose-dependent manner, compared with LDL-C levels < 70 mg/dL. Specifically, participants with LDL-C levels ≥ 160 mg/dL demonstrated a 43% increased risk of the composite outcome and a 2.25-fold higher risk of myocardial infarction compared to those with LDL-C levels < 70 mg/dL. Among statin users, LDL-C levels > 130 mg/dL were associated with an increased risk of the composite outcome. Conclusions: This study highlights the significant association between elevated LDL-C levels and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients undergoing dialysis. These findings underscore the importance of close monitoring and proactive management of LDL-C levels in this high-risk population. Future research should focus on developing tailored lipid-lowering strategies to improve cardiovascular outcomes in these patients.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; dialysis; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; outcome; statin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and clinical outcomes in patients with liver cirrhosis: a nationwide cohort study.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2551813. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2551813. Epub 2025 Aug 30. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40884310 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Lowering for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Among Men With Primary Elevations of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels of 190 mg/dL or Above: Analyses From the WOSCOPS (West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study) 5-Year Randomized Trial and 20-Year Observational Follow-Up.Circulation. 2017 Nov 14;136(20):1878-1891. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027966. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28877913 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Low Baseline Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol on Long-Term Postdischarge Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Sep 6;11(17):e025958. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.025958. Epub 2022 Aug 24. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 36000434 Free PMC article.
-
Quality improvement strategies for diabetes care: Effects on outcomes for adults living with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 31;5(5):CD014513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014513. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37254718 Free PMC article.
-
Chronotherapy versus conventional statins therapy for the treatment of hyperlipidaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 26;11(11):CD009462. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009462.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27888640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naghavi M., Ong K.L., Aali A., Ababneh H.S., Abate Y.H., Abbafati C., Abbasgholizadeh R., Abbasian M., Abbasi-Kangevari M., Abbastabar H., et al. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403:2100–2132. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mach F., Baigent C., Catapano A.L., Koskinas K.C., Casula M., Badimon L., Chapman M.J., De Backer G.G., Delgado V., Ference B.A., et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk: The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Eur. Heart J. 2019;41:111–188. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz455. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grundy S.M., Stone N.J., Bailey A.L., Beam C., Birtcher K.K., Blumenthal R.S., Braun L.T., de Ferranti S., Faiella-Tommasino J., Forman D.E., et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139:e1046–e1081. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000000624. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arnett D.K., Blumenthal R.S., Albert M.A., Buroker A.B., Goldberger Z.D., Hahn E.J., Himmelfarb C.D., Khera A., Lloyd-Jones D., McEvoy J.W., et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140:e596–e646. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

