Clinical Impact of Viscoelastic Testing in Liver Transplantation: A Before-and-After Study of Transfusion Needs and Outcomes
- PMID: 40725575
- PMCID: PMC12295854
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14144882
Clinical Impact of Viscoelastic Testing in Liver Transplantation: A Before-and-After Study of Transfusion Needs and Outcomes
Abstract
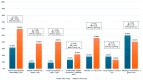
Background/Objectives: Liver transplantation (LT) is often complicated by severe bleeding and coagulopathy. Viscoelastic testing (VET) offers real-time, bedside assessment of coagulation and may improve transfusion management compared to standard tests. This study evaluates the clinical impact of VET implementation during liver transplantation on bleeding, transfusion requirements, complications, and mortality in a single Eastern European tertiary transplant center. Methods: We conducted a single-center before-and-after study comparing patients undergoing LT before and after the implementation of VET. All procedures were performed by the same surgical and anesthetic team using a standardized protocol. Data were collected retrospectively for the Before VET group and prospectively for the After VET group. We compared transfusion requirements, bleeding, complications, and mortality. Results: A total of 59 patients were included, 22 in the After VET group and 37 in the Before VET group. VET implementation was associated with lower intraoperative blood loss (median 4000 mL vs. 6000 mL, p = 0.017) and reduced red blood cell (RBC) transfusion volume (670 mL vs. 1000 mL, p = 0.008). FFP (0.23 vs. 1.59 units, p = 0.007) and platelet use (0.68 vs. 1.81 units, p = 0.035) were also significantly lower in the VET group, while fibrinogen use was higher (3.00 g vs. 2.00 g, p = 0.036). No differences were observed in complication rates or mortality at 30 days and 1 year in this small before-and-after study. Conclusions: VET improved transfusion precision and individualized coagulation management during LT, leading to reduced use of blood products. These findings support the adoption of VET as a standard of care in LT protocols, as it may enhance patient safety, even though no differences in postoperative complications or mortality were observed.
Keywords: bleeding; liver transplantation; transfusion; viscoelastic testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Desmopressin use for minimising perioperative blood transfusion.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 10;7(7):CD001884. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001884.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28691229 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological interventions for the prevention of bleeding in people undergoing elective hip or knee surgery: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 16;1(1):CD013295. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013295.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38226724 Free PMC article.
-
Tranexamic acid for preventing postpartum haemorrhage after caesarean section.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 13;11(11):CD016278. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD016278. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39535297 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative medical therapy before surgery for uterine fibroids.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 15;11(11):CD000547. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000547.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 04;4:CD000547. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000547.pub3. PMID: 29139105 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prophylactic platelet transfusion for prevention of bleeding in patients with haematological disorders after chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;2012(5):CD004269. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004269.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22592695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pustavoitau A., Lesley M., Ariyo P., Latif A., Villamayor A.J., Frank S.M., Rizkalla N., Merritt W., Cameron A., Dagher N., et al. Predictive Modeling of Massive Transfusion Requirements During Liver Transplantation and Its Potential to Reduce Utilization of Blood Bank Resources. Anesth. Analg. 2017;124:1644–1652. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001994. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources