Arthroscopic Arthrolysis of the Knee Joint Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 40725610
- PMCID: PMC12295493
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14144917
Arthroscopic Arthrolysis of the Knee Joint Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
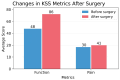
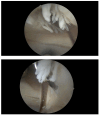
Background: Arthrofibrosis, mixed contracture, and patellofemoral impingement are frequent complications following total knee arthroplasty (TKA), potentially leading to chronic pain and poor recovery of range of motion (ROM). The comprehensive management of these complications remains challenging and controversial. Methods: This study analyzed the outcomes of arthroscopic arthrolysis performed in 27 patients diagnosed with arthrofibrosis, mixed contracture, and patellofemoral impingement post-TKA to evaluate the efficacy of this technique in improving knee function, enhancing ROM, and reducing pain, as assessed by the Knee Society Score (KSS). A total of 27 patients underwent arthroscopic arthrolysis following unsuccessful conservative rehabilitation. The arthroscopic procedure included removal of fibrous adhesions within the suprapatellar pouch, restoration of medial and lateral gutters, and lateral retinacular release of the patella. Intensive physiotherapy and continuous passive motion commenced immediately postoperatively. The mean follow-up period ranged from 24 to 60 months. Pain and functional outcomes were evaluated using KSSs. Results: Clinical improvements were evident in 26 cases, with the Knee Society Score rising from a preoperative average of 48 to 86, and pain scores improving from 30 to 41. Only one patient did not experience positive outcomes following the procedure. Arthroscopic arthrolysis appears beneficial for patients suffering from arthrofibrosis, patellofemoral impingement, and mixed contracture post-TKA, significantly improving clinical pain scores and KSS outcomes. Conclusions: Further research is recommended to refine specialized surgical instruments and enhance arthroscopic arthrolysis techniques.
Keywords: arthrofibrosis; arthroscopic management strategies; knee stiffness following total knee arthroplasty; patellofemoral impingement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information Total Knee Replacement. [(accessed on 15 November 2024)]; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499896/
-
- Global Market Insights Total Knee Replacement Market Report. [(accessed on 2 March 2025)]. Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/total-knee-replacement-market.
-
- McMahon S.E., Doran E., O’Brien S., Cassidy R.S., Boldt J.G., Beverland D.E. Seventeen to Twenty Years of Follow-Up of the Low Contact Stress Rotating-Platform Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Cementless Tibia in All Cases. J. Arthroplast. 2019;34:508–512. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.11.024. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

