Assessing LLMs on IDSA Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Comparison Study
- PMID: 40725688
- PMCID: PMC12295083
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14144996
Assessing LLMs on IDSA Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Comparison Study
Abstract
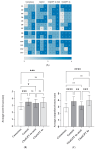
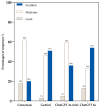
Background: Native vertebral osteomyelitis (NVO) presents diagnostic and therapeutic challenges requiring adherence to complex clinical guidelines. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) offers new avenues for real-time clinical decision support, yet their utility in managing NVO has not been formally assessed. Methods: This study evaluated four LLMs-Consensus, Gemini, ChatGPT-4o Mini, and ChatGPT-4o-using 13 standardized questions derived from the 2015 IDSA guidelines. Each model generated 13 responses (n = 52), which were independently assessed by three orthopedic surgeons for accuracy (4-point scale) and comprehensiveness (five-point scale). Results: ChatGPT-4o produced the longest responses (428.0 ± 45.4 words), followed by ChatGPT-4o Mini (392.2 ± 97.4), Gemini (358.2 ± 60.5), and Consensus (213.2 ± 68.8). Accuracy ratings showed that ChatGPT-4o and Gemini achieved the highest proportion of "Excellent" responses (54% and 51%, respectively), while Consensus received only 20%. Comprehensiveness scores mirrored this trend, with ChatGPT-4o (3.95 ± 0.79) and Gemini (3.82 ± 0.68) significantly outperforming Consensus (2.87 ± 0.66). Domain-specific analysis revealed that ChatGPT-4o achieved a 100% "Excellent" accuracy rating in therapy-related questions. Statistical analysis confirmed significant inter-model differences (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Advanced LLMs-especially ChatGPT-4o and Gemini-demonstrated high accuracy and depth in interpreting clinical guidelines for NVO. These findings highlight their potential as effective tools in augmenting evidence-based decision-making and improving consistency in clinical care.
Keywords: ChatGPT; Gemini; IDSA guidelines; artificial intelligence; clinical decision support; large language models; native vertebral osteomyelitis; spine infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of large language models in patient education and clinical decision support for rotator cuff injury: a two-phase benchmarking study.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025 Aug 4;25(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12911-025-03105-5. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025. PMID: 40760478 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking the performance of large language models in uveitis: a comparative analysis of ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4.0, Google Gemini, and Anthropic Claude3.Eye (Lond). 2025 Apr;39(6):1132-1137. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-03545-9. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Eye (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39690303
-
ChatGPT-4o outperforms gemini advanced in assisting multidisciplinary decision-making for advanced gastric cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025 Aug;51(8):110096. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2025.110096. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40294561
-
Stench of Errors or the Shine of Potential: The Challenge of (Ir)Responsible Use of ChatGPT in Speech-Language Pathology.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jul-Aug;60(4):e70088. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70088. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40627744 Review.
-
Applications and Concerns of ChatGPT and Other Conversational Large Language Models in Health Care: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Nov 7;26:e22769. doi: 10.2196/22769. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39509695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deutscher Ärzteverlag GmbH Spondylodiscitis: Diagnosis and Treatment Options. [(accessed on 29 March 2024)]. Available online: https://www.aerzteblatt.de/int/archive/article/195481.
-
- Braun S., Diaremes P., Schönnagel L., Caffard T., Brenneis M., Meurer A. Spondylodiscitis. Orthopadie. 2023;52:677–690. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

