Concurrent Acute Appendicitis and Cholecystitis: A Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 40725712
- PMCID: PMC12296163
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14145019
Concurrent Acute Appendicitis and Cholecystitis: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
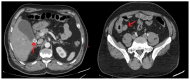
Background: This systematic review aimed to comprehensively evaluate the clinical, diagnostic, and therapeutic features of synchronous acute cholecystitis (AC) and acute appendicitis (AAP). Methods: The review protocol was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251086131) and conducted in accordance with PRISMA 2020 guidelines. A systematic search was performed across PubMed, MEDLINE, Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Google databases for studies published from January 1975 to May 2025. Search terms included variations of "synchronous," "simultaneous," "concurrent," and "coexistence" combined with "appendicitis," "appendectomy," "cholecystitis," and "cholecystectomy." Reference lists of included studies were screened. Studies reporting human cases with sufficient patient-level clinical data were included. Data extraction and quality assessment were performed independently by pairs of reviewers, with discrepancies resolved through consensus. No meta-analysis was conducted due to the descriptive nature of the data. Results: A total of 44 articles were included in this review. Of these, thirty-four were available in full text, one was accessible only as an abstract, and one was a literature review, while eight articles were inaccessible. Clinical data from forty patients, including two from our own cases, were evaluated, with a median age of 41 years. The gender distribution was equal, with a median age of 50 years among male patients and 36 years among female patients. Leukocytosis was observed in 25 of 33 patients with available laboratory data. Among 37 patients with documented diagnostic methods, ultrasonography and computed tomography were the most frequently utilized modalities, followed by physical examination. Twenty-seven patients underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy and appendectomy. The remaining patients were managed with open surgery or conservative treatment. Postoperative complications occurred in five patients, including sepsis, perforation, leakage, diarrhea, and wound infections. Histopathological analysis revealed AAP in 25 cases and AC in 14. Additional findings included gangrenous inflammation and neoplastic lesions. Conclusions: Synchronous AC and AAP are rare and diagnostically challenging conditions. Early recognition via imaging and clinical evaluation is critical. Laparoscopic management remains the preferred approach. Histopathological examination of surgical specimens is essential for identifying unexpected pathology, thereby guiding appropriate patient management.
Keywords: acute appendicitis; acute cholecystitis; concurrent diseases; diagnostic modalities; laparoscopy; simultaneous diseases; synchronous diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment for acute appendicitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 29;4(4):CD015038. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015038.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38682788 Free PMC article.
-
Single-incision versus conventional multi-incision laparoscopic appendicectomy for suspected uncomplicated appendicitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 5;11(11):CD009022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009022.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39498756
-
Abdominal drainage to prevent intraperitoneal abscess after appendectomy for complicated appendicitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 11;4(4):CD010168. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010168.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40214287
References
-
- Fitz R.H. Perforating Inflammation of the Vermiform Appendix: With Special Reference to Its Early Diagnosis and Treatment. Kessinger Publishing; Whitefish, MT, USA: 1886. p. 321.
-
- Błaszczyszyn K., Bińczyk W., Dróżdż O., Siudek B., Grzelka M., Pupka D., Orzechowski J. Simultaneous laparoscopic management of coexisting cholecystitis and appendicitis-a case report. Qual. Sport. 2024;18:53470. doi: 10.12775/QS.2024.18.53470. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

