Right and Left Side-Lying Positioning During Bottle-Feeding in Premature Infants-A Randomized Crossover Pilot Study
- PMID: 40725801
- PMCID: PMC12295368
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14145108
Right and Left Side-Lying Positioning During Bottle-Feeding in Premature Infants-A Randomized Crossover Pilot Study
Abstract
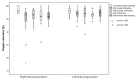
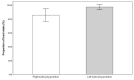
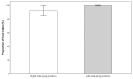
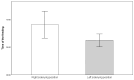
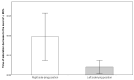
Background/Objectives: Optimal feeding position may contribute to improving the quality and safety of bottle-feeding in premature infants. The aim of this study was to compare the advantages of right side-lying (R-SLP) and left side-lying (L-SLP) positioning during the bottle-feeding of preterm infants. Methods: The randomized study included eight neonates (n = 8) born at ≤34 weeks of gestational age (GA). Four bottle-feeding sessions were conducted for each newborn: two in the R-SLP and two in the L-SLP position. Levels of oxygen saturation (SpO2) and heart rate (HR) were measured as indicators of physiological stability. The qualitative aspects of feeding included total time of SpO2 declines to ≤85%, the newborn's alertness level based on the Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS), and the number of possetings, regurgitations, and choking episodes. The volume of milk consumed and the duration of each feeding session were also recorded. Results: The L-SLP position was characterized with higher SpO2 (p = 0.042) at the 10th minute after feeding and lower HR (p = 0.022) at the end of feeding. Greater milk intake (p = 0.042), shorter feeding duration (p = 0.021), and shorter duration of SpO2 declines to ≤85% (p = 0.025) were also observed in L-SLP. No differences were found in alertness level, or in the number of choking episodes, possetings, or regurgitations compared to R-SLP. Conclusions: This pilot study suggests the potential efficacy of the L-SLP position during bottle-feeding of premature infants. The results require the need for larger studies to confirm the potential benefits of using L-SLP.
Keywords: bottle-feeding; oral feeding; premature infant; side-lying position.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

