Differential Role of CD318 in Tumor Immunity Affecting Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Compared to Other Adenocarcinomas
- PMID: 40725832
- PMCID: PMC12295231
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14145139
Differential Role of CD318 in Tumor Immunity Affecting Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Compared to Other Adenocarcinomas
Abstract
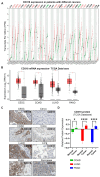
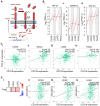
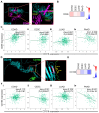
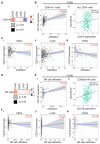
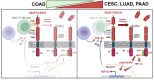
Background/Objectives: CD318 (also known as CDCP1) is a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in many cancers and contributes to tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis by activating SRC family kinases through phosphorylation. Emerging evidence also suggests that CD318 plays a role in modulating the tumor immune microenvironment, although its precise mechanism in tumor progression is still not well understood. Methods: To investigate this, we analyzed the expression and immune-related functions of CD318 using the publicly available data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) across colorectal adenocarcinoma (COAD), cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), and pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD). Results: All four cancers exhibited a high level of CD318 expression. Notably, in CESC, LUAD, and PAAD, plasmin-mediated cleavage of CD318 leads to phosphorylation of SRC and protein kinase C delta (PKCδ), which activates HIF1α and/or p38 MAPK. These downstream effectors translocate to the nucleus and promote the transcriptional upregulation of TGFβ1, fostering an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment through Treg cell recruitment. In contrast, this signaling cascade appears to be absent in COAD. Instead, our analysis indicate that intact CD318 in COAD interacts with the surface receptors CD96 and CD160, which are found on CD8+ T cells and NK cells. Conclusions: This interaction enhances cytotoxic immune responses in COAD by promoting CD8+ T cell and NK cell activity, offering a possible explanation for the favorable prognosis associated with high CD318 expression in COAD, compared to the poorer outcomes observed in CESC, LUAD, and PAAD.
Keywords: CDCP1/CD318; PKCδ; SRC; T and NK cells; TGFβ1; overall survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Sahdeo Prasad was employed by R&D Life Sciences. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression predicts poor prognosis of colon adenocarcinoma and is associated with PD-L1 expression and lymphocyte infiltration.PeerJ. 2025 Jun 30;13:e19550. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19550. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40611940 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring potential therapeutic targets for colorectal tumors based on whole genome sequencing of colorectal tumors and paracancerous tissues.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 4;12:1605117. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1605117. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40688112 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the role of GPCR signaling in metabolic reprogramming and immune microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma: a multi-omics study with experimental validation.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1606125. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1606125. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40547013 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

